News & Highlights
Leveraging the LanM process model to quantify economic impact of REE selectivity
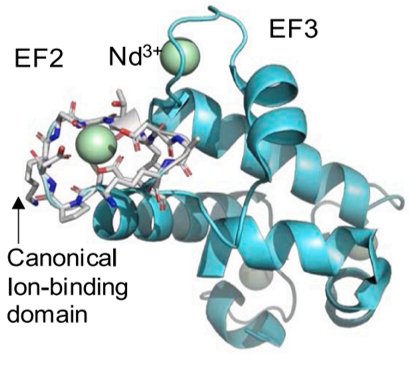 Research Highlight
Research Highlight
Established a computational pipeline for predicting REE selectivity of lanmodulin variants
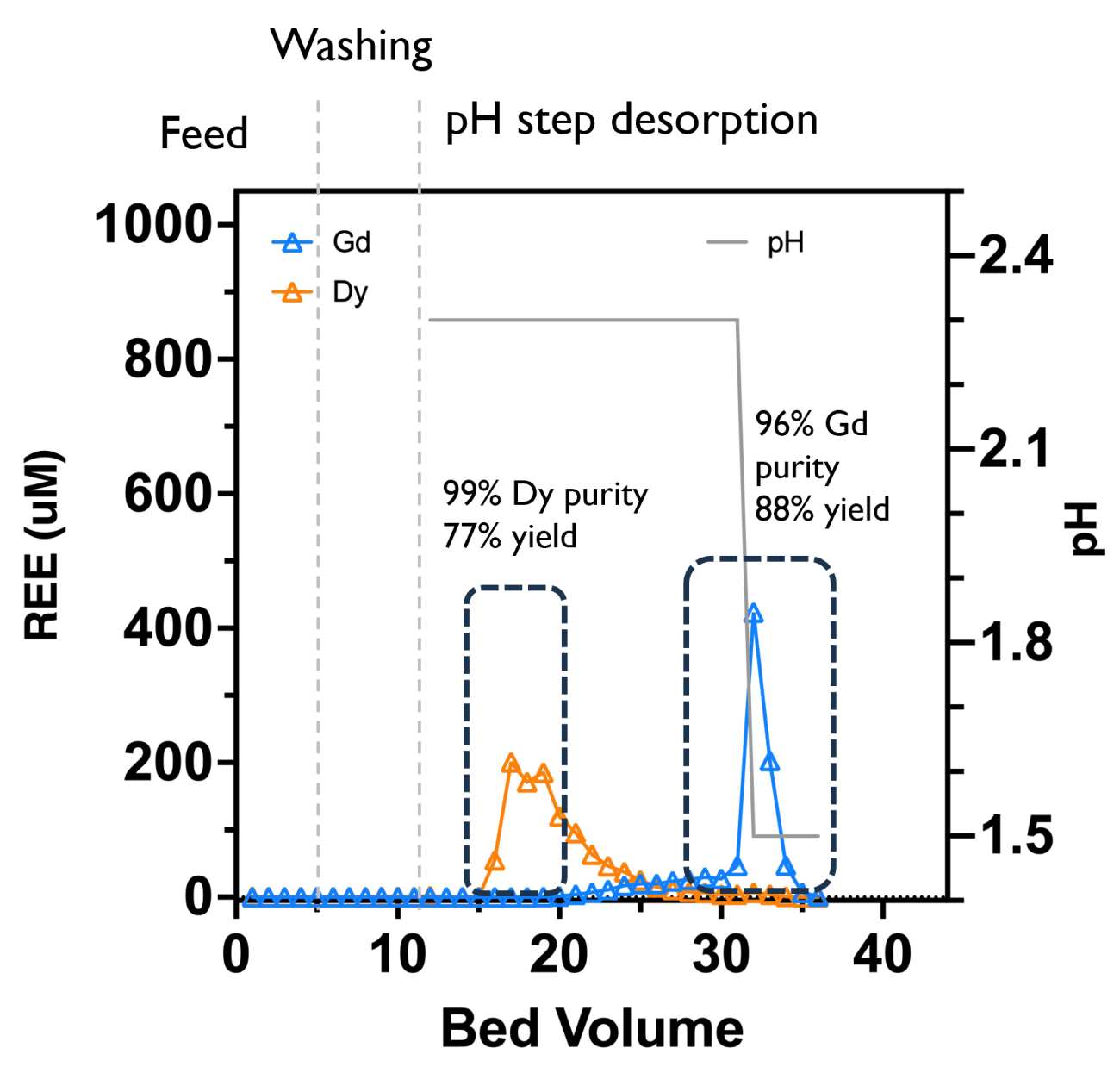 Research Highlight
Research Highlight
New lanmodulin variant enables single-stage Gd vs Dy separation
 In the News
In the News
LLNL: Inspired by nature, proteins pick out mission-critical metals
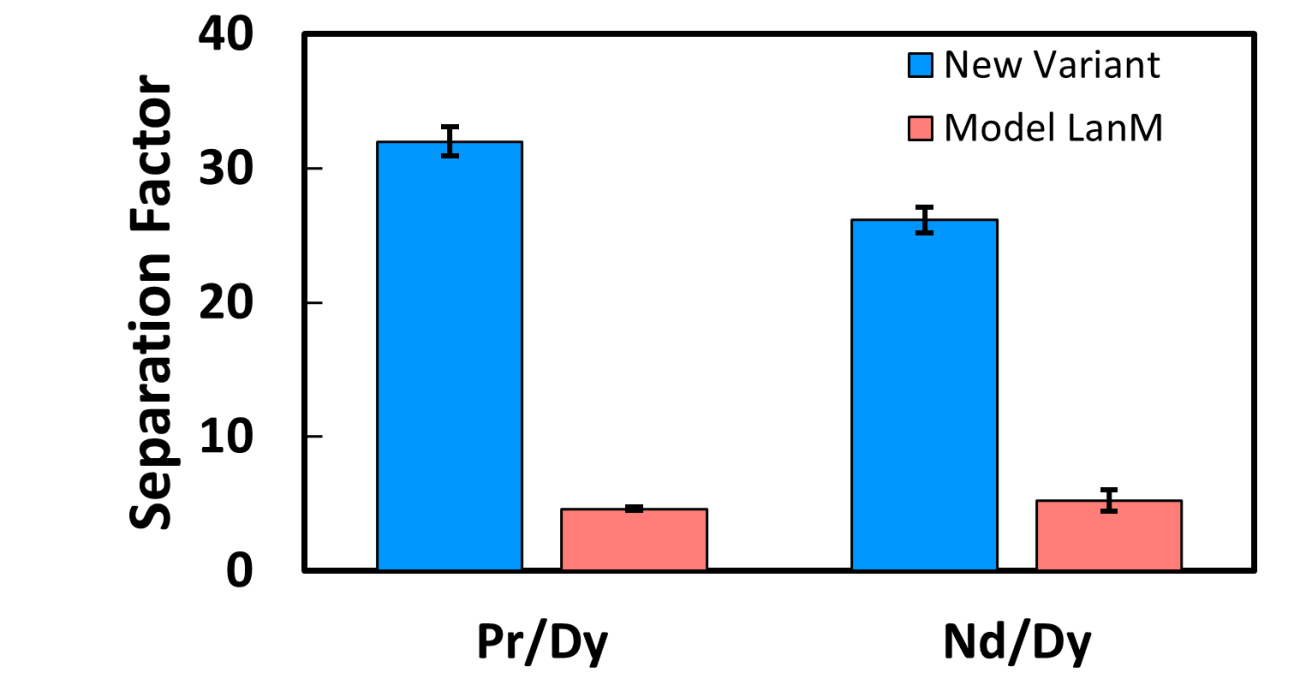 Research Highlight
Research Highlight
New lanmodulin variant yield more efficient separations
The goal of this project is to develop an economical and environmentally sustainable protein-based process for rare earth element (REE) separation from electronic waste (E-waste). Researchers will target separations that range from relatively “easy” (i.e., neodymium (Nd) v. dysprosium (Dy)) to highly challenging (i.e., Dy v. terbium (Tb), and Nd v. praseodumium (Pr)) using size-reduced lanmodulin proteins. By combining the acid-free leaching process with the all-aqueous protein-based REE separation process, researchers anticipate the development of an end-to-end process with significantly lower chemical consumption and environmental impact relative to conventional hydrometallurgical processes.
