CMI researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
Integrating the Lanmodulin (LanM) process model with TEA to inform variant selection and for separation process optimization.
Achievement
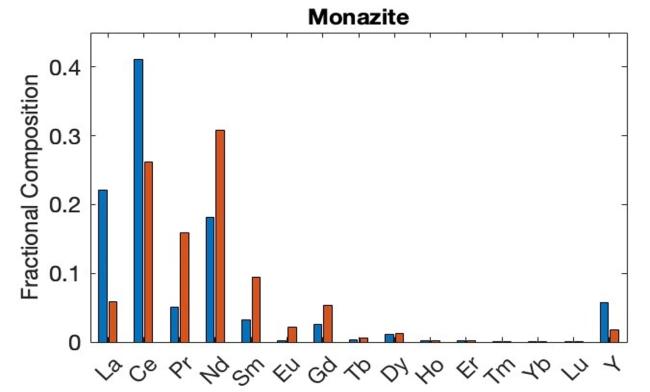
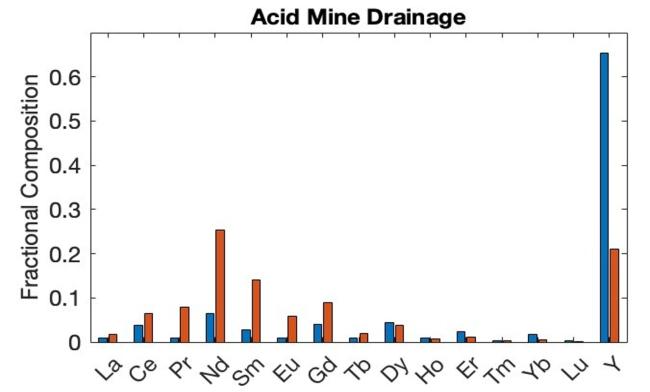
The thermodynamic adsorption model and REE oxide prices were used to quantify the economic impact of using a La/Ce-rejecting LanM variant to extract REE from two feedstocks with distinct REE compositions. The LanM variant upgrades the value of both feedstocks by preferentially extracting middle REEs.
Significance and Impact
Allows the economic impact of a specific LanM variant to be estimated for a specific REE feedstock without experimentation. Expanding to a column-based flow model will help determine the optimal column operation procedure for a given REE feedstock composition, LanM variant, and column capacity.
Hub Target Addressed
Developing highly selective separation from complex sources.