CMI at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Penn State and TdVib conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
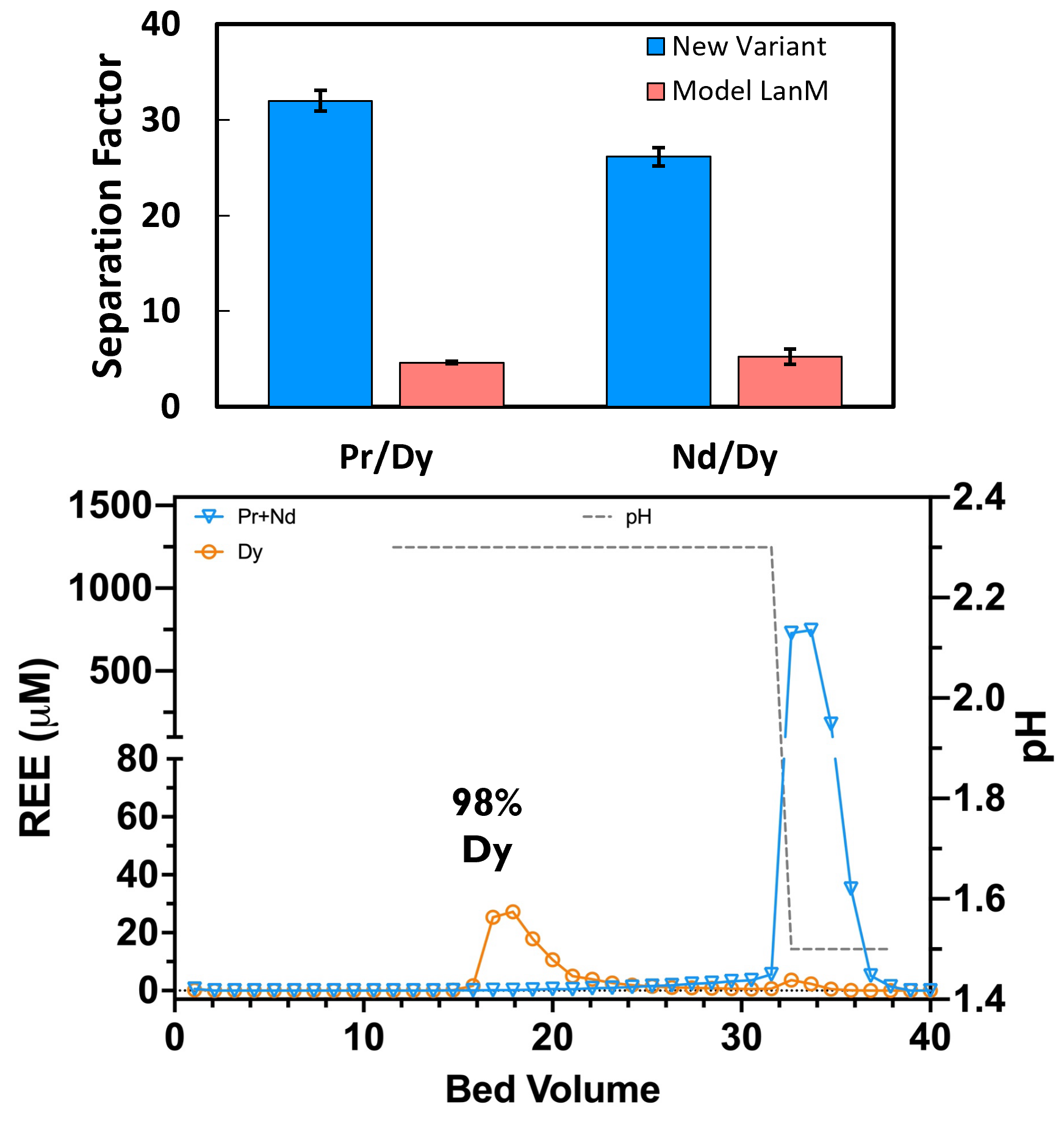
Exceptional selectivity of new lanmodulin (LanM) variant enables high-purity Dy separation from a mixed rare earth oxide (mREO) prepared from a wind turbine magnet using CMI’s Acid-free Dissolution Recycling process.
Achievement
Discovered new LanM variant with >5-fold improvement in Dy/Nd and Dy/Pr selectivity. Starting with a mREO with 6% Dy and 94% NdPr, a single adsorption/desorption cycle generated a Dy fraction (98% purity, 80% yield) and a NdPr fraction (99.5% purity, 99% yield).
Significance and Impact
Higher selectivity enables more efficient separation, meaning lower water and chemical consumption.
Hub Target Addressed
Developing highly selective separation from complex sources.