CMI researchers at Idaho National Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight
Innovation
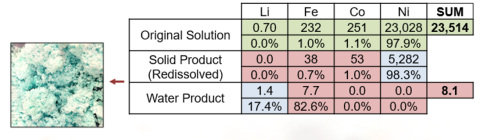
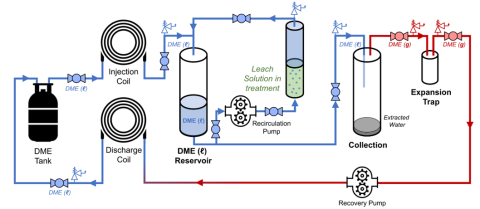
Dimethyl ether (DME) used to remove water and crystallize solids from a Ni-rich recycling stream derived from electrochemical leaching of lithium-ion battery (LIB) black mass.
Achievement
Production of high purity and low-moisture solid (metal content 98.3% nickel) and highly purified water.
Significance and Impact
Opportunity to achieved closed loop water reuse during critical materials processing.
Hub Target Addressed
Advancing environmentally friendly and efficient recovery of critical materials from end‐of‐life energy storage devices