CMI researchers at Ames National Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight
Innovation
Identified an effective method to improve the mechanical properties of Ce-Co-Fe-Cu gap magnet.
Achievement
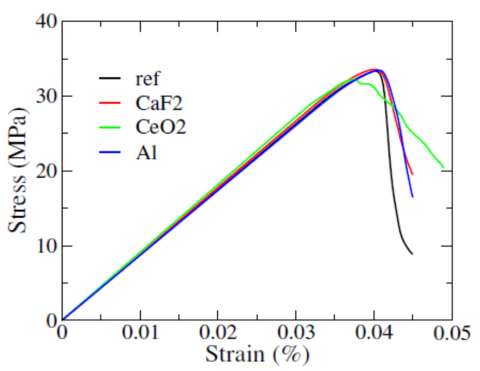
- Additives CaF2 and Al improve mechanical properties by arresting crack growth while CeO2 deflects crack path during propagation.
- The additives improve fracture strain by 3 – 8%, compared with a reference sample.
Significance and Impact
- Ce-Co-Fe-Cu is a potential “gap” magnet suitable for many applications including vehicle auxiliary motors.
- Improved mechanical properties will enhance reliability in service conditions.
- Tougher Ce-Co-Fe-Cu magnets will also reduce materials losses during manufacturing and post-manufacturing processing.
Hub Goal Addressed
Increase speed of discovery and integration.