CMI researchers at Idaho National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
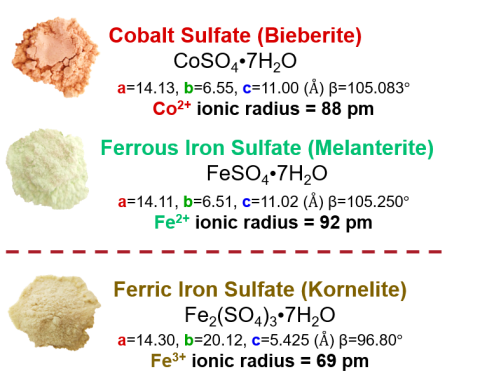
Crystal structure is a key factor for separations in Co and Fe sulfate solutions with dimethyl ether (DME) fractional crystallization.
Achievement
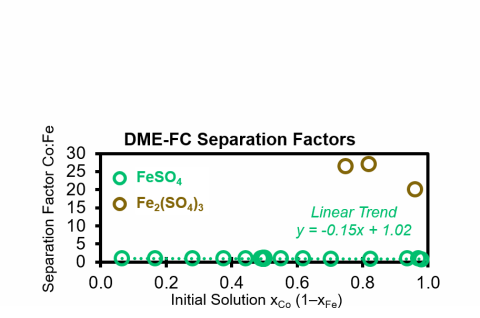
- High separation factors (αCo:Fe>20) are obtained via DME-FC of metal salts with dissimilar crystal lattices and ionic radii, i.e., CoSO4 and Fe2(SO4)3.
- Adjacent elements with interchangeable lattices and ionic radii, e.g., CoSO4 and FeSO4, show lower separation factors (αCo:Fe≈0.9-1.1).
Significance and Impact
Improved capability to design selective capture of high value critical materials in crystal matrices.
Hub Target Addressed
Advancing next-generation atom- and energy-efficient separations.