CMI researchers at the University of Arizona conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
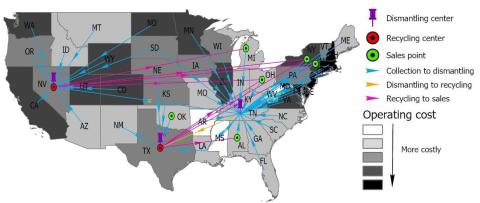
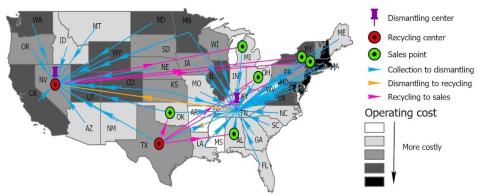
A risk-averse stochastic program model and a Benders decomposition algorithm were developed to design a resilient reverse logistics supply chain network for NdFeB magnet recycling under the COVID-19 supply chain disruptions.
Achievement
- The model suggests the optimal facility locations, processing capacities, inventory levels, and material flows for NdFeB magnet recyclers that could meet >99% of the demand.
- While adding a facility and increasing inventory level would add costs, it may improve long term business profit and resilience.
- A manuscript describing this work has been published in the journal Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review
Significance and Impact
Optimization of the NdFeB reverse logistics supply chain network will create a more sustainable business under disruptive events like COVID-19.
Hub Goals Addressed
Modeling and analyses to optimize the economic value and environmental impact of CMI technologies.