CMI researchers at Purdue University, Arizona State University and Ames Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight
Innovation
Use techno-economic assessment (TEA) and life cycle assessment (LCA) to evaluate and improve economic and environmental sustainability of novel acid-free dissolution recycling technology.
Achievements
- Copper nitrate identified as a major cost driver, environmental hotspot.,
- Material cost reduced by 11% by recycling copper nitrate.
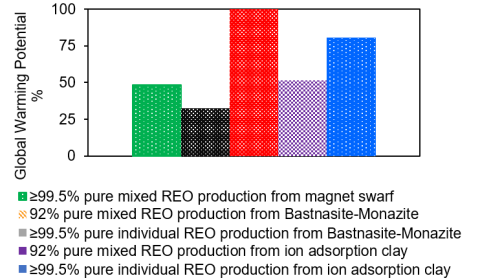
- Improved environmental sustainability when compared to traditional rare earth element (REE) production.
Significance and Impact
Acid-free dissolution recycling of magnet swarf can create a sustainable pathway for REE production from waste materials.
Hub Goals Addressed
- Increase speed of discovery and integration.
- Recover and convert into high value end products.

