This CMI research was conducted at Ames Laboratory
Achievement
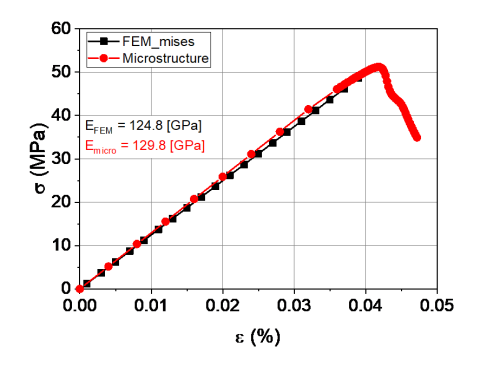
A finite-element (FE) model was developed for a SmCo5 magnet matrix with Sm2O3 impurities. The results accurately predict the stress distribution from a three-point bend analysis to identify domains of stress concentration and failure.
Significance and impact
The model for the SmCo5 with Sm2O3 magnets allows for rapid assessment of the mechanical properties with computational time reduced by several orders of magnitude compared to microstructural modeling. Novel and innovative architectural layouts can be developed to maximize mechanical strength.
Details and next steps
Several other architectures of SmCo5 with Sm2O3, such as laminated and core-shell, will be simulated to support experimental efforts by the SmCo Fracture Toughness Project.
