![Structures of the homoleptic [Dy(DGA3)]3+ complexes optimized in the gas phase showing alkyl-alkyl interactions.](/sites/default/files/styles/large/public/inline-images/cmi-highlight-353a.png?itok=mDjev_4q)
CMI researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Idaho National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
Extraction chromatography (EXC) as alternative for rare earth separations.
Achievement
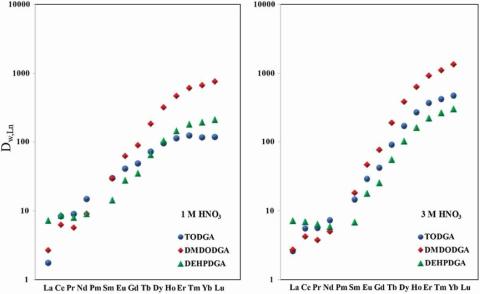
Using computations combined with spectroscopy and extraction experiments, a study of diglycolamide (DGA) extractants impregnated into EXC resins revealed structural details of how DGA molecules bind to rare earth metal ions.
Significance and Impact
- EXC resins using DGA extractants offer a selective, low-cost alternative to traditional ion exchange resins.
- Molecular structure of the DGA complexes with rare earths depends on DGA structure, degree of loading, and anion.
- Loading strongly favors heavy rare earths.
Hub Target Addressed
Unlocking unconventional resources; selective separations for complex mixtures.