CMI researchers from Idaho National Laboratory and Colorado School of Mines conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
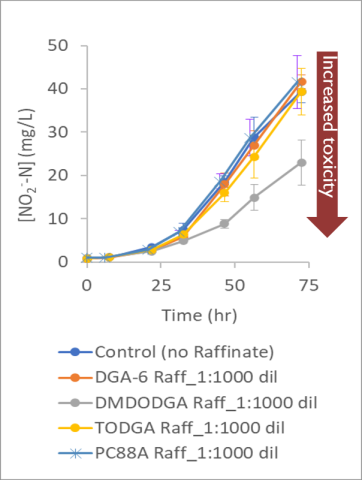
Determined that variations in length and structure of alkyl sidechains in diglycolamide (DGA) extractants can significantly impact the apparent toxicity of raffinates to a model wastewater treatment organism.
Achievement
- Compared the impacts of surrogate solvent extraction raffinates (prepared without REE) on the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea.
- Discovered that raffinates with DGAs having all four alkyl chains ≥C6 did not affect ammonia oxidation, while raffinate containing a DGA with two one-carbon (methyl) groups (N, N’-Dimethyl-N,N’-dioctyldiglycolamide; DMDODGA) was inhibitory.
Significance and Impact
Findings such as these provide guidance to ligand designers seeking to mitigate downstream waste and environmental liabilities.
Hub Target Addressed
- Minimizing hazardous chemical use and waste generation.
- Assessing economic, environmental, and social acceptance impacts.
