CMI researchers from Idaho National Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight.
Innovation
Developed and demonstrated ion exchange protocols for separation of metals from a leachate of lithium-ion battery (LIB) black mass prepared using organic acid biolixiviant in electrochemical cell (EC).
Achievement
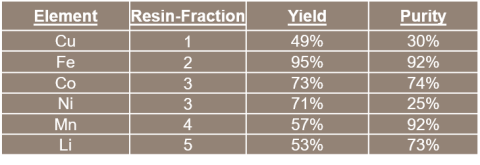
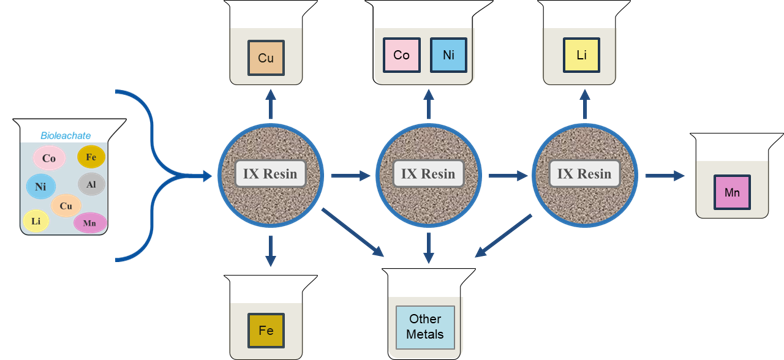
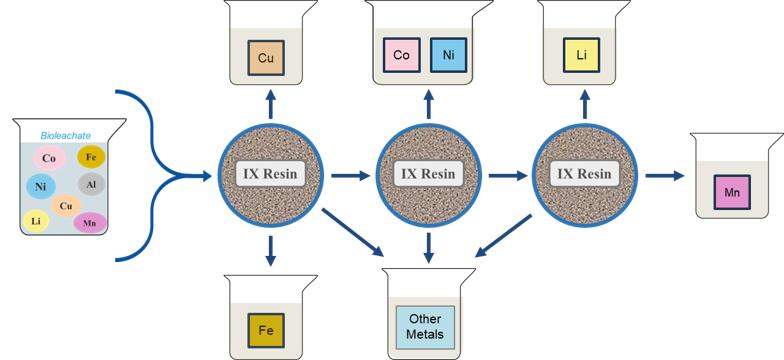
The EC-bioleachate was passed through a sequence of three ion exchange (IX) resins to effectively remove Fe and Cu and isolate three high purity metal streams: (1) Co + Ni, (2) Mn and (3) Li.
Significance and Impact
- EC-bioleaching results in lower Fe and Cu contamination compared to bioleaching alone, facilitating a relatively simple ion exchange sequence to isolate high value metal streams.
- High metal yield and purity can improve economics of LIB bioleaching and increase the potential for commercialization of the process.
Hub Target Addressed
Green recovery strategy for domestic recycling of LIB metals.