CMI researchers at Idaho National Laboratory, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and Pennsylvania State University conducted the research for this highlight
Innovation
Developed a biological approach for Nd/Dy separation.
Achievement
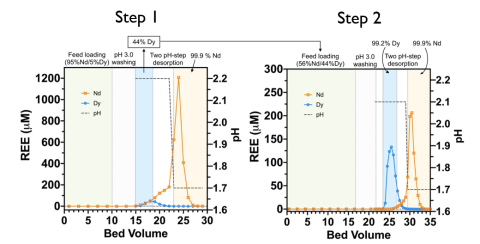
5:95 mixture of Dy:Nd separated into high purity Dy (99.2%) and Nd (99.9%) fractions using two column steps with immobilized lanmodulin protein.
Significance and Impact
- All-aqueous method for tandem extraction and separation of rare earth elements (REE) critical to clean energy technologies.
- High REE selectivity of lanmodulin offers potential to unlock low-grade unconventional REE sources.
- Approach will be extended to E-waste feedstock and coupled with bioleaching for sustainable process development.
Hub Target Addressed
Sustainable method for REE recycling from end-of-life consumer products.
Dong, Z., Mattocks, J.A., Deblonde, G., Dehong, H., Jiao, Y., Cotruvo, J.A.*, and Park, D.M.* Bridging Hydrometallurgy and Biochemistry: A Protein-based Process for Recovery and Separation of Rare Earth Elements, ACS Central Science (In Press).
