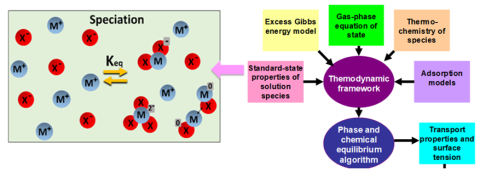
CMI researchers from OLI Systems, Rutgers University and Arizona State University conducted the research for this highlight.
Innovation
Established comprehensive thermodynamic model for aqueous REEs containing both inorganic and organic ligands.
Achievement
- Predicts solubility, complexation equilibria, and acid-base equilibria in close agreement with experimental data
- Valid for a wide range of pH, salt concentration, temperature, and pressure for oxalates, citrates, and acetates
- Process simulations run on ordinary desktop computer.
Significance and Impact
Accurate tool for designing and optimizing separation processes for production and recycling of REEs and for predicting REE properties in geological and biological settings.
Hub Target Addressed
Develop and deploy scientific tools that accelerate the development of relevant technologies.
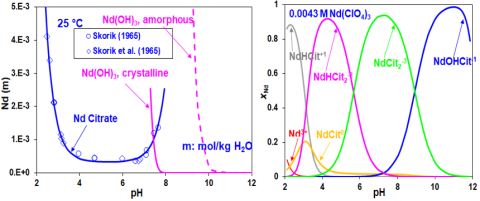
Right: Neodymium citrate complexes tunable with pH
