CMI researchers from Idaho National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
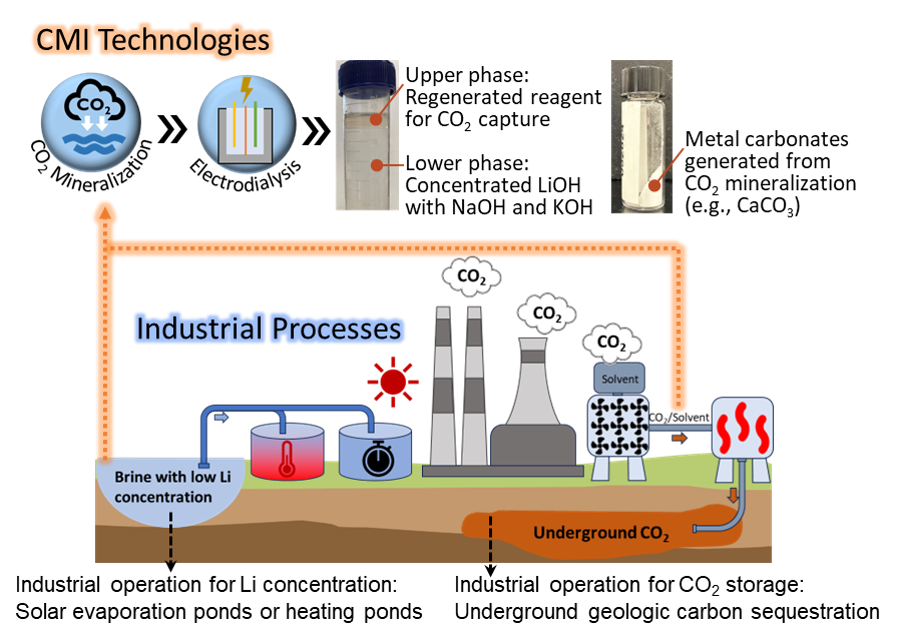
The most common industrial carbon capture technology relies on absorption of CO2 from flue gas by an aqueous amine. The CO2 is typically subsequently released by heating the solution, and then the CO2 must be compressed and transported for storage. These steps have high energy costs. Instead, we use the CO2-loaded amine to react with dilute lithium brines, which converts the carbon into insoluble metal carbonates (e.g., CaCO3, MgCO3). Electrodialysis is then used to regenerate the amine and produces a more concentrated Li solution.
Achievement
- Recycled >75% of the reagent used for CO2 capture.
- Demonstrated >4-fold Li concentration with a surrogate solution (140 mg/L to 580 mg/L).
Significance and Impact
- Utilizing and mineralizing captured CO2, at lower energy cost than conventional carbon sequestration.
- Reducing chemical usage and environmental impact through regeneration of reagent.
Hub Target Addressed
Efficient use of energy and water.