CMI researchers at Rutgers and Arizona State University conducted the research for this highlight
Innovation
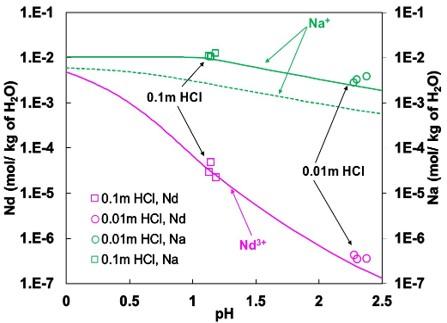
A comprehensive study combining experimental measurement and thermodynamic modeling of the solubility of sodium neodymium fluoride (NaNdF4), a material useful for more efficient production of Nd metal.
Achievement
The aqueous solubility of NaNdF4 was measured experimentally. This data, in conjunction with literature data for Na and Nd fluorides, and solid-state thermodynamics we measured, was used to model the thermodynamics of aqueous species in the system. This work is published in the Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data 2025, 70, 4483-4498).
Significance and Impact
- Rare earth fluorides are important both in process development (e.g., for rare earth metallization) and in direct applications (e.g., lasers, imaging, fiber optics).
- OLI’s simulation platform can now be used to optimize processes that include NaNdF4 or any subsystems involving Na, Nd, and F-related species.
Hub Target Addressed
Developing and applying scientific tools to accelerate technology.