CMI researchers from Idaho National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
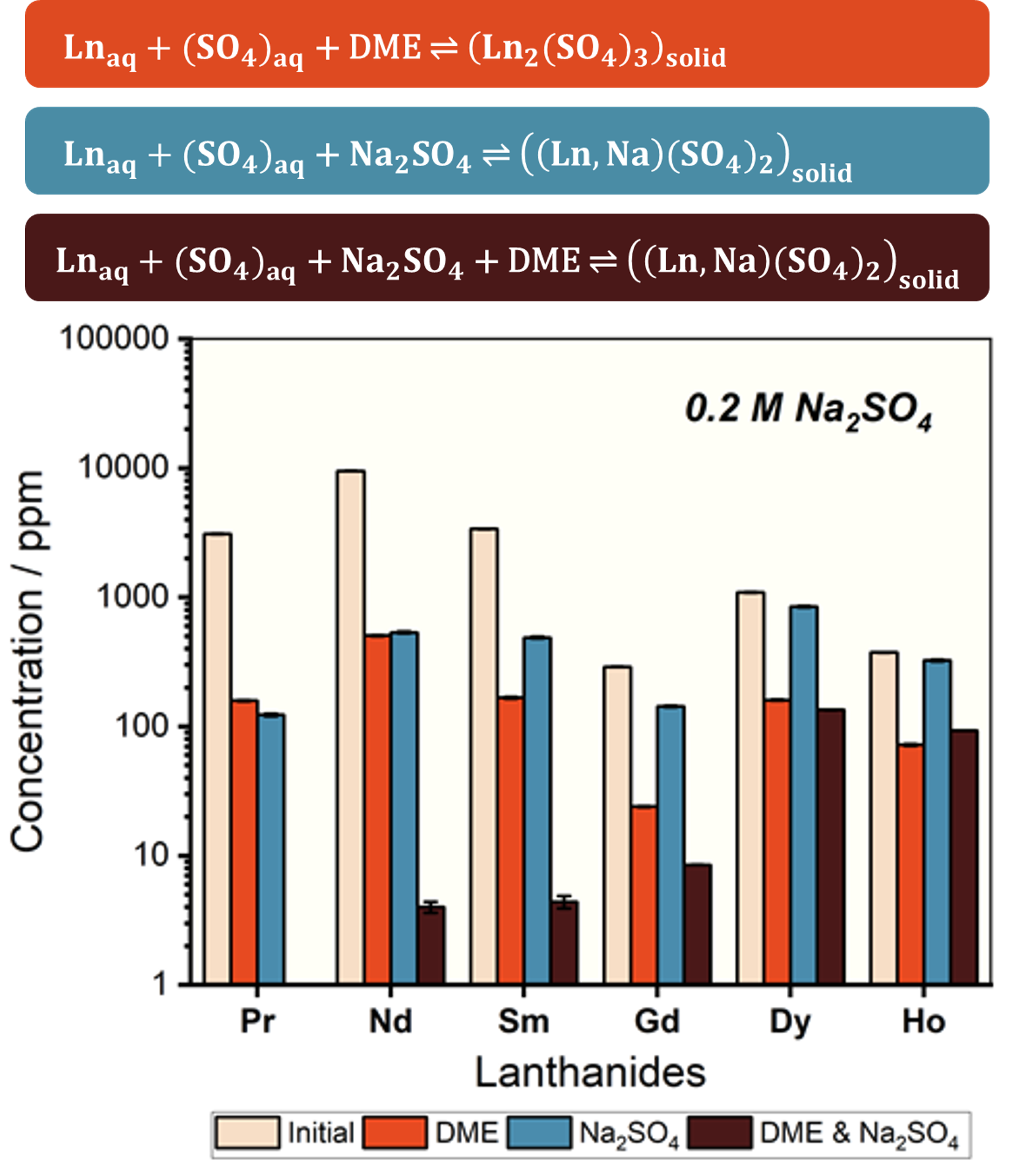
Integrate recyclable crystallization trigger (dimethyl ether, DME) and reactive precipitation agent (Na2SO4) for synergistic recovery of dilute rare earth elements (REEs).
Achievements
1) Synergistic REE recovery can reduce the effective saturation solubility limit to <10 ppm concentrations, lower than achieved by either trigger alone. 2) Determined optimal initial Na2SO4 concentration to induce REE precipitation in presence of DME.
Significance and Impact
- DME FC integrated with Na2SO4 can recover low concentration REEs from unconventional sources (acid mine drainage, industrial wastewater, and mining byproducts) as well as enhance recovery from conventional sources.
- Next Steps: Optimize operating conditions, including pressure and temperature, to maximize REE yield and selectivity.
Hub Target Addressed
Minimizing hazardous chemical use and waste generation.