CMI researchers at Ames National Laboratory, the University of Arizona, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Niron and Powdermet conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
Hot pressing was assessed as a scalable, cost-effective, and energy-efficient alternative to spark plasma sintering (SPS) for Sm2Fe17N3 magnet production.
Achievement
- Hot pressing Sm2Fe17N3 magnet shows similar densities and magnetic properties with SPS: Hci=10.9 kOe, and BHmax=24 MGOe at small scale.
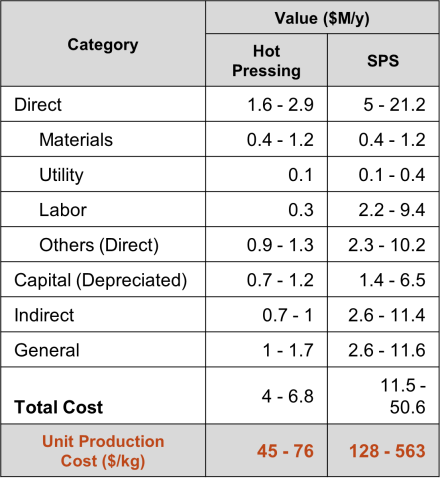
- Since hot pressing is easily scaled compared to SPS, techno-economic analysis (TEA) and life cycle assessment (LCA) assumed production of 90 metric tons of Sm2Fe17N3 magnets per year.
- Hot pressing reduced production costs by 65% - 86% compared to SPS due to reduced labor and capital costs.
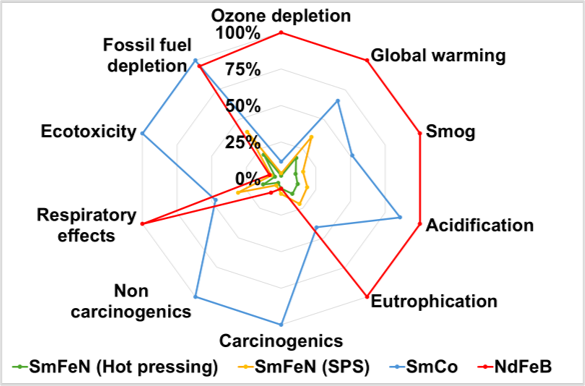
- Hot pressing reduced environmental impacts compared to SPS.
Significance and Impact
- Recommended hot pressing for sintering Sm2Fe17N3 magnet.
- Next step is to experimentally validate scalability.
Hub Target Addressed
- Accelerated magnet discovery and maturation.
- Assessing economic, environmental, and social acceptance impacts.