CMI researchers at Idaho National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
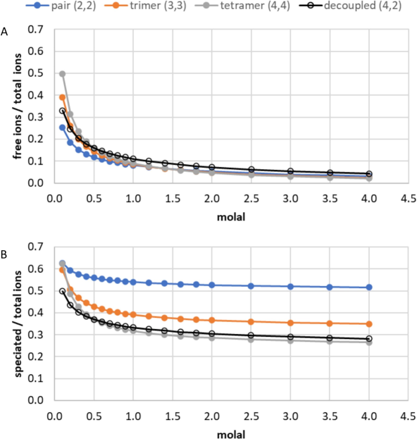
Expanded the stepwise hydration solution model from simple 1:1 salts (e.g., NaCl) to more complex 2:2 (e.g., MnSO₄) and 3:2 salts (e.g., Nd₂(SO₄)₃), with direct relevance to critical material production.
Achievements
- Developed an equilibrium cluster model that separates solute concentration function (e.g. reaction order) from final cluster size, making calculations more straightforward.
- Demonstrated that Debye–Hückel long-range interactions and mass action ion pairing, though mechanistically different, are mathematically similar.
Significance and Impact
Advancing mechanistic models of solutions at high concentration/saturated conditions will facilitate development of approaches for crystallization and precipitation (e.g., dimethyl ether fractional crystallization) as well as other separations.
Hub Target Addressed
- Minimizing hazardous chemical use and waste generation
- Efficient co-recovery of materials
Aaron D. Wilson, Mouad Arrad, Anthony S. Wexler, "Step-wise Hydration: Comparison of Debye-Hückel Long-Range interactions and ion pairing," Journal of Molecular Liquids (2025) 127805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2025.127805.