CMI researchers from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
Phosphogypsum (PG) is a bulk currently unutilized waste stream generated during fertilizer production from the mined phosphate rock. PG contains critical rare earth elements (REE) trapped in the gypsum matrix. Currently, there exists no process for their recovery and purification.
Achievement
- Demonstrated quantitative recovery and purification of REE from the 3 M HNO3 PG leachate with diglycolamide (DGA) solvent extraction technology.
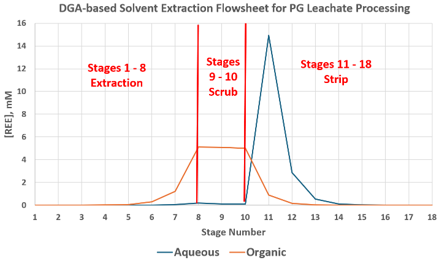
- Developed a prototypical REE solvent extraction flowsheet model for the continuous processing of the PG leachate.
Significance and Impact
The developed DGA-based flowsheet model parameters:
- REE recovery from PG leachate: >99%
- REE concentration factor: >15
Hub Target Addressed
Developing processes to recover and separate REEs from traditional or unconventional sources.