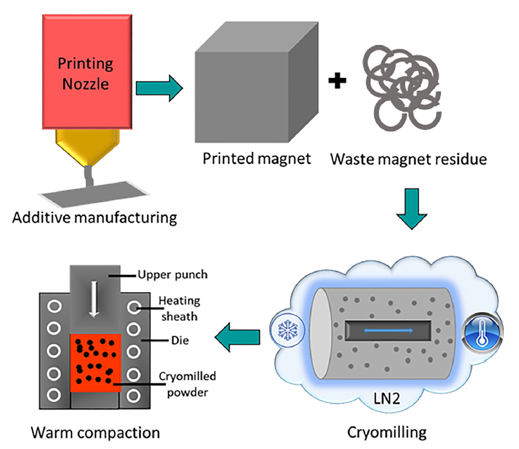
Schematics of the recycling process of AM bonded magnets
This CMI-funded research was conducted at Ames Laboratory and Oak Ridge National Laboratory, in a collaboration between CMI projects Additive Manufacturing of Polymer Bonded Magnets (2.1.11) and Recovery of Critical Materials from Dilute Electronic Waste Streams (3.3.13).
Achievement:
Successfully demonstrated recycling of additively manufactured (AM) rare earth magnets with nearly 100% yield and no magnet degradation
Significance and Impact:
- Reduced manufacturing wastage and potentially offset any rare earth element demand and low production costs
- Research advances efforts to ensure sustainability in critical materials by forming a close loop supply chain
Details and Next Steps:
- Remanent magnetization and saturation magnetization increased by 4% and 6.5% respectively, due to enhanced density by 6% while coercivity and energy product were retained from the original additive printed bonded magnets
- Being extended to anisotropic AM gap magnets

