CMI researchers at Idaho National Laboratory and Colorado School of Mines conducted the research for this highlight
Innovation
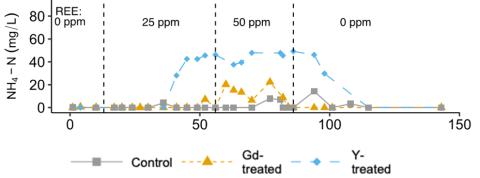
Observed that high (≥1 µM) soluble concentrations of yttrium or gadolinium caused transient inhibition of microbial ammonia removal, and changes in abundance of specific microbial populations.
Achievement
In bioreactors simulating aerobic wastewater treatment, 50 ppm Y or Gd additions impaired ammonia oxidation, but after cessation of REE treatment, microbial communities recovered.
Significance and Impact
For REE-laden industrial or mining waters that could reach the environment, site-specific studies of ecological impacts may be warranted.
Hub Target Addressed
Supporting environmentally sustainable technologies for critical material processing.
Salmon, O.; Rasmussen, K.; Aurelius, S.; Vanzin, G.; Munakata-Marr, J.; Fujita, Y., 2022. ACS ES&T Water 2022. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestwater.2c00098
