CMI researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and Case Western Reserve University conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
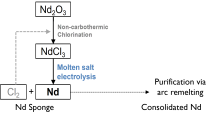
First fully sustainable Nd electrowinning process enabled by novel reactor designs and a dimensionally stable anode that reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Achievement
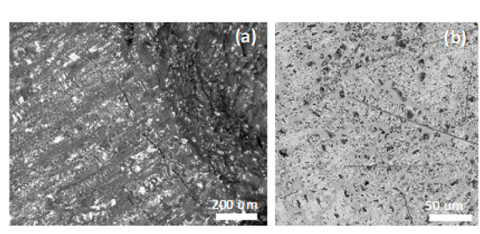
Arc-melting process enabled the production of Nd metal (95 atomic percent purity achieved) without Cl residue from electrowon Nd.
Significance and Impact
- Nd metal production at 2.3 kWh/kg energy consumption vs. 3.3 kWh/kg state-of-art, with corresponding GHG reduction.
- Eliminated Cl from deposit, increasing Nd purity to >95 at.% in large regions.
- Significantly reduced GWP as confirmed through LCA .
Hub Goal Addressed
Energy-efficient rare earth metals production.