CMI researchers from the Idaho National Laboratory, Ames National Laboratory, and University of Idaho conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
Carbon-based electrodes demonstrated preferential electrosorption of REEs, enabling selective separation from competing metal ions.
Achievement
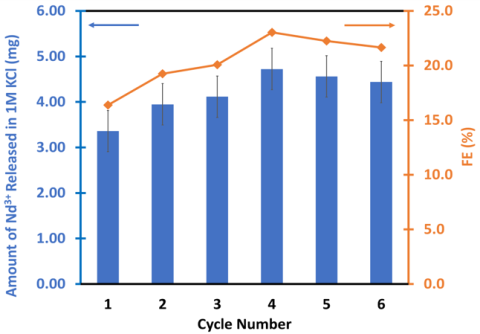
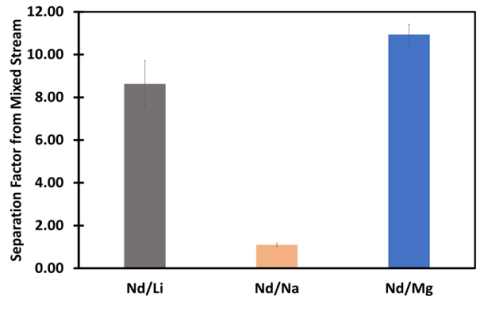
Pseudocapacitive sorption of REEs on soft carbon electrodes was tested for immobilization and recovery of Nd from dilute aqueous solutions. The results showed that beyond cyclability for Nd adsorption and release, the pseudocapacitive process also provides selectivity for Nd over competing ions such as Na, Li, and Mg.
Significance and Impact
A potential new approach for the recovery of REEs from dilute aqueous sources with minimal chemical and energy consumption.
Hub Target Addressed
Grand challenge of developing highly selective separation from complex sources.