CMI researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight
Innovation
Develop chelators that can selectively recognize and leach large over small rare earth elements (REEs) from mineral sources.
Achievement
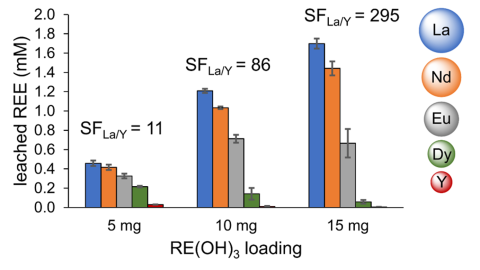
- Selective leaching of light, large REEs from caustically cracked synthetic REE phosphate (REE hydroxide) by a new size-selective lixiviant, acyclopa.
- Single-pass separation factor (SF) of 295 between La and Y, large and small REEs, respectively, that are abundant in monazite and xenotime minerals.
Significance and Impact
- Paves the way towards extracting individual REEs selectively from RE minerals, eliminating the use of non-selective brute-force leaching methods (e.g., strong mineral acid dissolution) and reducing reliance on downstream energy-intensive solvent extraction for REE separation.
- Next step: optimize leaching conditions to further increase SFs; develop 2nd generation derivatives with higher leaching capacity.
Hub Target Addressed
Unlocking unconventional resources; highly selective separation from complex sources; intra-REE separation.