CMI researchers at University of Tennessee, Knoxville, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight
Achievement
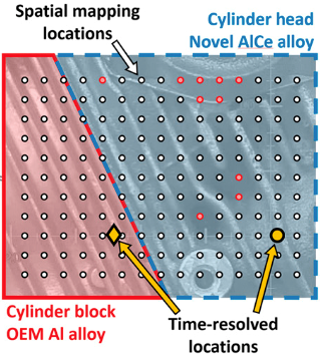
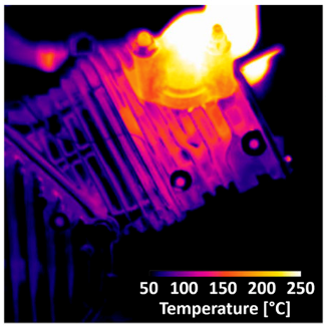
A first-of-a-kind in-operando technique has been developed for understanding Al-Ce alloy strain behavior in a cylinder head at elevated temperature in a running internal combustion engine.
Significance and impact
This research demonstrates lattice-strain measurement within the volume of Al-Ce alloy components by neutron diffraction under extreme conditions. The microstructure resists coarsening at elevated temperatures, enabling observation of load and stress distribution. Improvements can lead to uses for Ce to improve profitability in mining.
Details and next steps
- Thermal expansion affected lattice strain. Used neutron diffraction to measure static and dynamic lattice strain.
- Development continues toward new alloy compositions tailored for engine applications.