CMI researchers from Idaho National Laboratory and OLI Systems conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
Thermodynamic simulations accelerate development of precipitation methods for separation of monovalent metal ions (e.g., Li, Na, K) by enabling understanding of the key reaction mechanisms.
Achievement
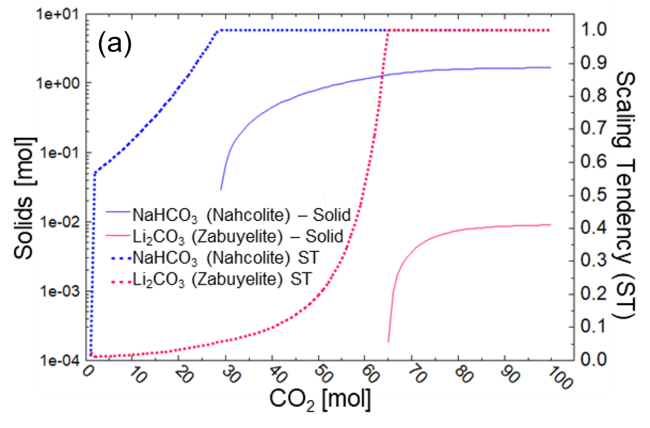
- The favored removal of Na+ compared to Li+ upon addition of CO2 to a synthetic brine solution was predicted by thermodynamic simulations that showed the lower solubility of NaHCO3 compared to Li2CO3.
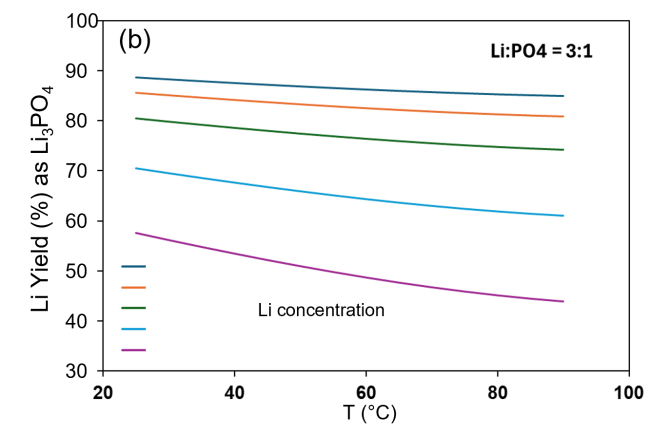
- Comparison of experimental observations and simulation predictions indicated that Li3PO4 precipitation is constrained by kinetics as well as thermodynamics.
Significance and Impact
Thermodynamic modeling enables more efficient experimental efforts by constraining the design space, resulting in reduced costs and waste generation.
Hub Target Addressed
Developing and applying scientific tools to accelerate technology maturation