CMI researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
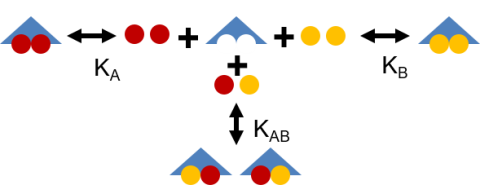
Developed and validated a mathematical model for binding REE to the two principal coordination sites of the bacterial protein lanmodulin.
Achievement
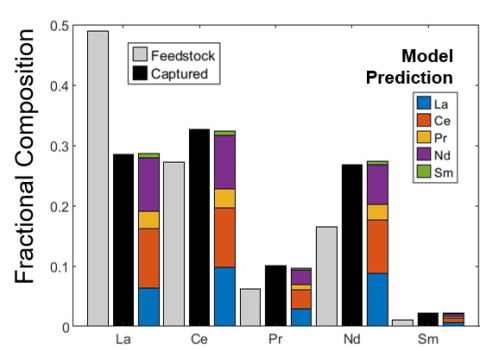
Characterized lanmodulin binding to pairwise combinations of 10 REEs over a range of concentration ratios. Homogenous and heterogenous equilibrium binding coefficients were derived from binary REE binding data through model fitting. Enabled accurate prediction of equilibrium distribution of REEs bound to lanmodulin from a range of feedstocks.
Significance and Impact
- This is an important first step in developing a process model for use in designing and scaling lanmodulin-based REE separations.
- Next steps: expand model development toward kinetic model for on-column REE adsorption and desorption.
Hub Target Addressed
Developing highly selective separation from complex sources.