CMI researchers from Ames National Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight.
Innovation
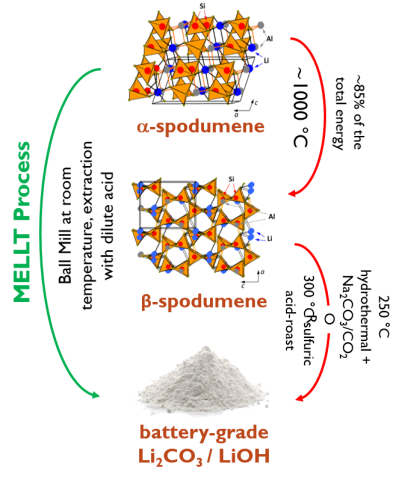
Disruptive mechanochemical process to extract 85+% of lithium available in domestic hard-rock ore.
Achievement
The MELLT process so far yields 75% lithium extraction from chemical-grade domestic α-spodumene at a 250 g scale with minimal acid usage and temperatures below 100 °C. Process cost savings are estimated at ~45% per ton of Li2CO3 produced.
Significance and Impact
- Elimination of the high-temperature thermal-decrepitation step.
- Avoidance of harsh acid/alkaline solutions with mild alternatives.
- Viable alternative to traditional energy- and waste-intensive methods for Li recovery from hard rock, greatly reducing energy costs.
Hub Target Addressed
Recovery and conversion of critical minerals into high-value end products. Industry adoption of technology for the source-diversification of lithium.
