CMI researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
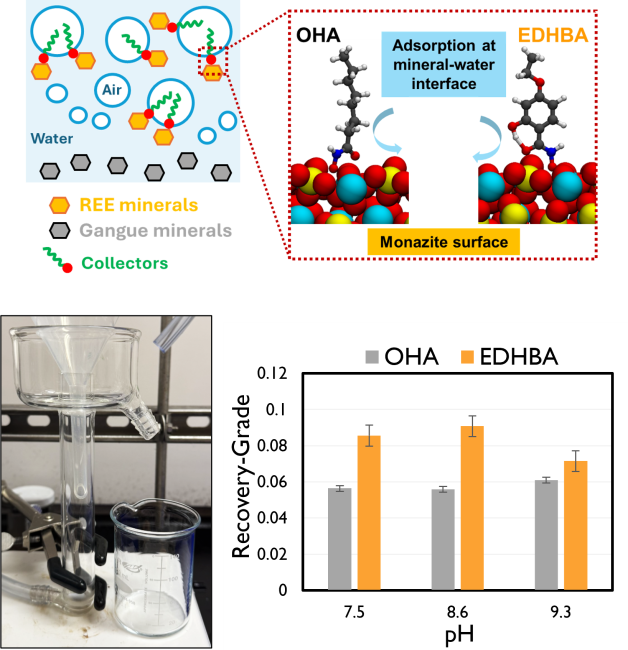
A combined experimental and computational approach reveals how hydroxamic acid adsorption drives flotation, guiding the optimal choice of collector for monazite.
Achievement
- Spectroscopic and computational methods uncovered how hydroxamic acid adsorption on monazite affects flotation
- Aliphatic OHA forms a denser, more strongly adsorbed layer, while aromatic EDHBA builds stable multilayers through stronger intermolecular forces.
- Microflotation experiments demonstrate that EDHBA exhibits better performance than OHA, achieving higher REE yield at basic pH with an improvement of 2-3%.
Significance and Impact
By elucidating how molecular-scale adsorption governs flotation behavior, this work provides a science-driven foundation for rational collector design.
Hub Target Addressed
Insights into adsorption inform collector design strategies that enable more efficient REE recovery from traditional or unconventional sources.