CMI researchers at Purdue University and Eck Industries lead the activity for this highlight with researchers at Colorado School of Mines
Innovation
Demonstrated a processing route for a high performance CMI alloy that is more environmentally friendly than the incumbent material.
Achievement
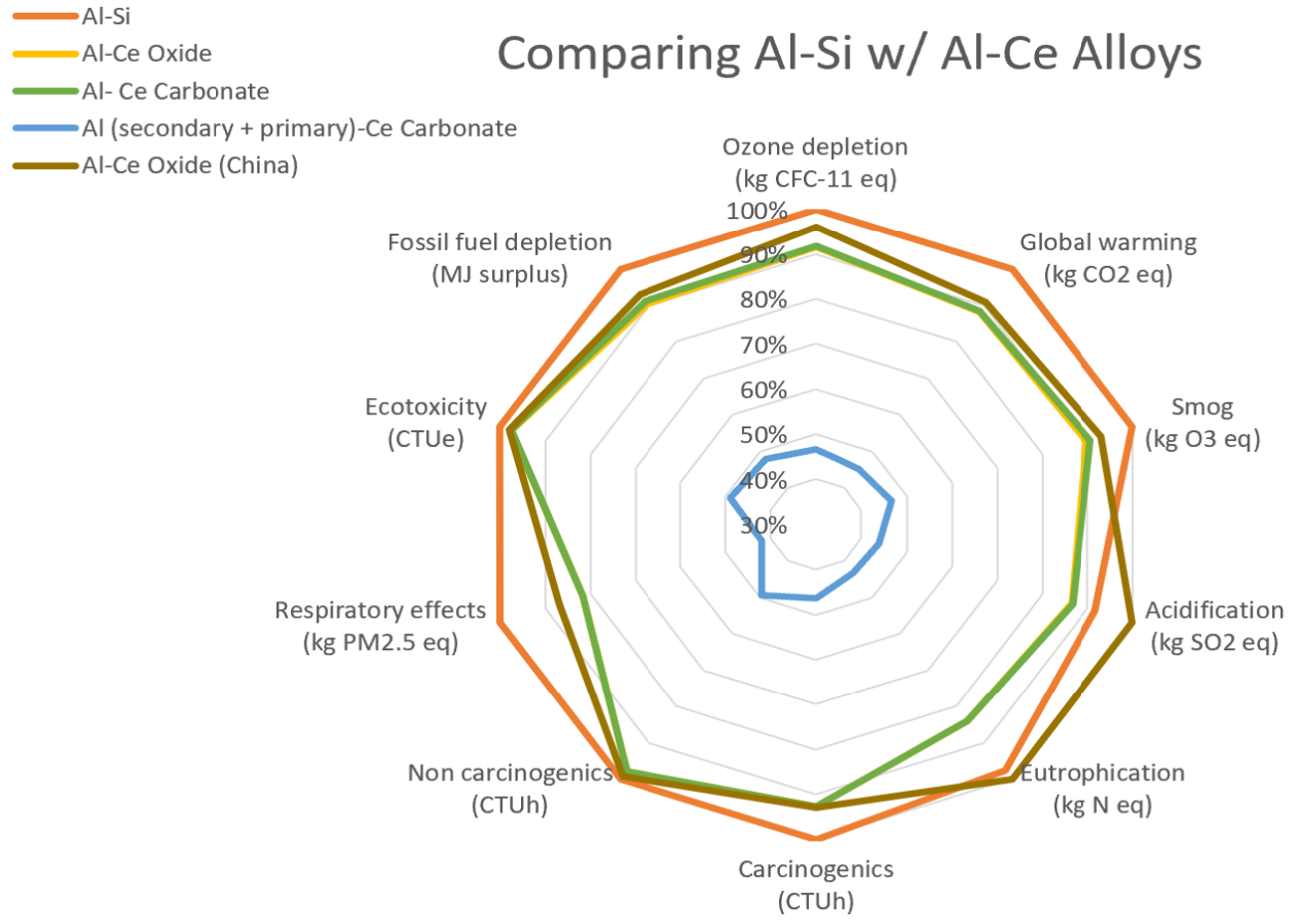
Conducted LCA for manufacturing Al-Ce alloys via direct reduction from CeO2or Ce2(CO3)3 and compared its impact to a conventional Al-Si alloy.
Significance and Impact
- Al-Ce alloys made from direct reduction of CeO2 or Ce2(CO3)3 perform better in all environmental categories compared to Al-Si alloys when sourced domestically.
- Use of secondary aluminum significantly (>35%) improves the environmental performance of the Al-Ce alloy across all categories.
- Loss of primary Al identified as a significant environmental hotspot.
Hub Target Addressed
Assessing the environmental sustainability of CMI technologies.
