CMI researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Idaho National Laboratory, Marshallton and Energy Fuels conducted the research for this highlight.
Innovation
More efficient lanthanide (Ln) separation using neutral extractants.
Achievement
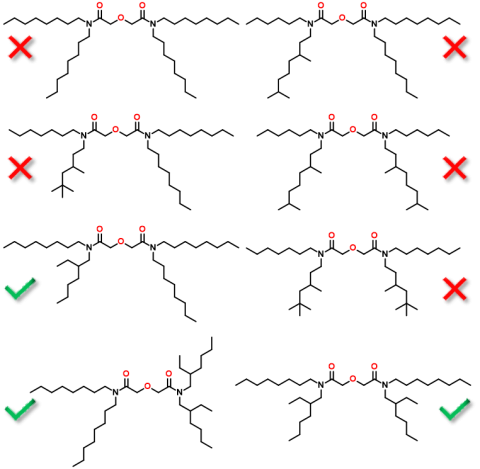
- Identified diglycolamides (DGAs) for use at high concentrations with good flow, extraction, and selectivity among light Lns.
- Incorporated special branched N-alkyl substituents in DGAs to allow high throughput in Ln separation from HCl feed solutions.
- Achieved comparable Ln loading capacity to industry standard2-ethylhexyl phosphonic acid-mono-2-ethylhexyl ester (PC88A).
- DGAs show ~2x higher selectivity compared to PC88A.
- Modifier disrupts Ln-DGA complex aggregation, preventing 3rd-phase formation and improving solvent viscosity.
Significance and Impact
Enables design of improved Ln separation processes with fewer stages (smaller footprint), less waste production, and lower cost.
Hub Target Addressed
Highly selective separation from complex sources.
