CMI researchers at Arizona State University conducted the activity for highlight
Innovation
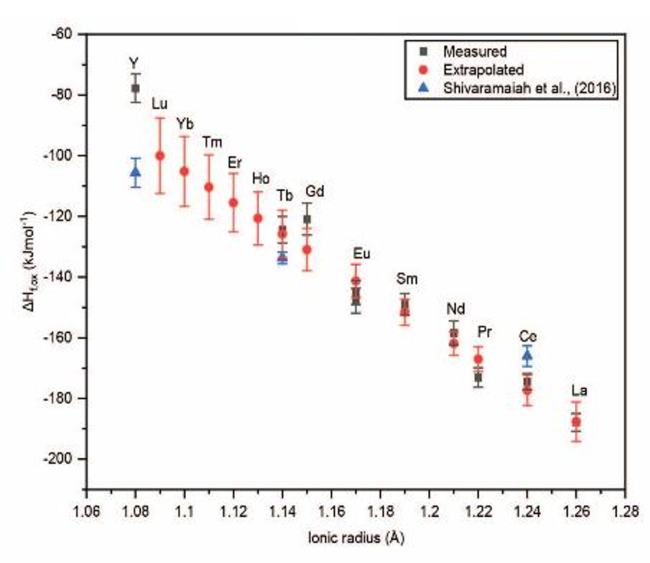
Synthesis and thermochemistry of REE carbonates (REECO3OH). Evaluation of structural and thermodynamic properties through experimental measurements and extrapolation to endmembers which could not be directly synthesized.
Achievement
Enthalpies of formation of REECO3OH (from oxides) have been determined using room temperature acid calorimetry.
Significance and Impact
- Carbonates are major REE ore minerals, understanding their thermodynamic stability is essential for modeling and application
- Understanding the thermodynamic properties of carbonate phases, such as kozoite, helps model the phase fractionation and mobility of REEs during ore mineral formation. This can lead to better models for geologists searching for new domestic REE deposits.
Hub Target Addressed
Developing and applying scientific tools to accelerate technology maturation.