CMI researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratory conducted the activity for this highlight
Innovation
Use of oil-soluble and water-soluble extractants, each selectively targeting heavy or light lanthanides (Lns), enhances the separation of adjacent Lns compared to traditional single-extractant methods.
Achievement
- Achieved significant REE loading in the extraction step, up to 0.16 M, using 0.5 M oil-soluble DGA-6 REE extractant.
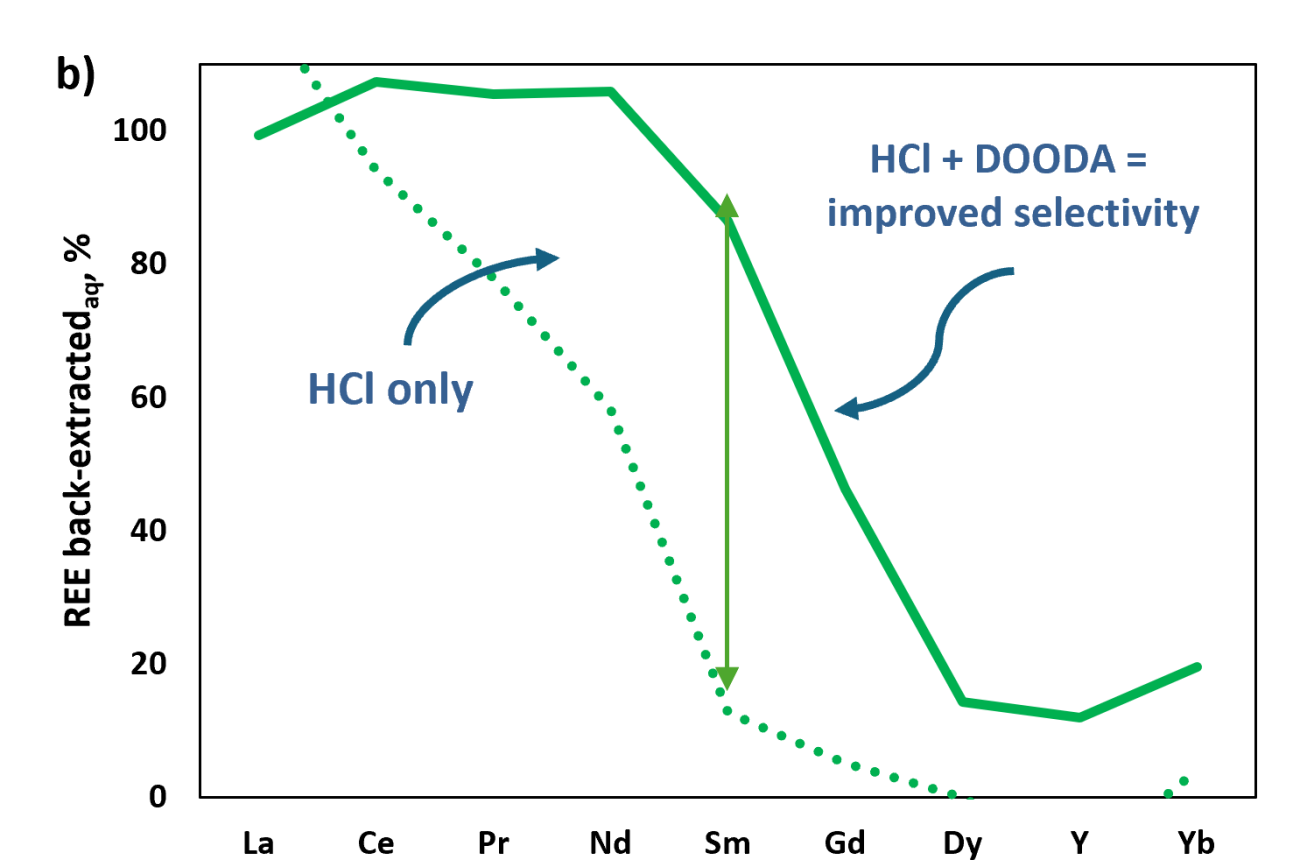
- Powerful aqueous complexant DOODA selectively back-extracts target REEs from the loaded DGA-6 solvent, achieving more than five times the recovery efficiency compared to using HCl alone.
- DOODA exhibits exceptional stability in 3 M HCl when complexed with REE, unchanged after 40 days.
Significance and Impact
Enables design of improved REE separation processes with fewer stages, reduced waste production, lower costs, and full chemical recyclability.
Hub Target Addressed
Highly selective separation from complex sources.