CMI researchers at Idaho National Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight
Achievement
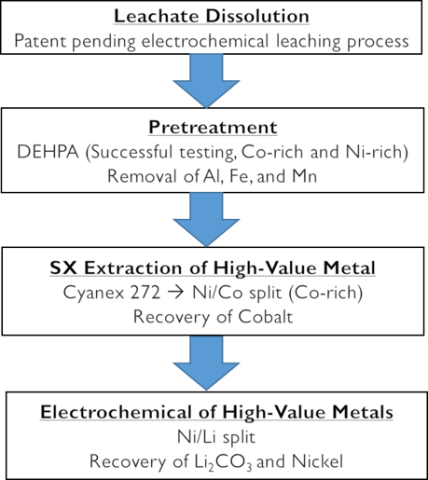
Complete technoeconomic analysis of different electrochemical lithium-ion battery (LiB) recycling scenarios were conducted based on 80,000 tons/year facility
Significance and impact
- Technology developed at INL based on Di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (DEHPA - an extractant agent) can enrich Co to 94.9% purity with a cost of $808/ton feed for the chemicals used in the process technology
- The feed cost dominates the economics. The breakeven cost of the feed is at $5.2/kg The process is highly profitable at $4 or less per kg of recycled LiB materials
Details and next steps
- Unit optimization is needed to enrich metals in this process to maximize purity and value of several metals.
- We will be updating and optimizing our TEA as we improve extraction and separation procedures.
