CMI researchers from Case Western Reserve University and University of Arizona conducted the research for this highlight.
Innovation
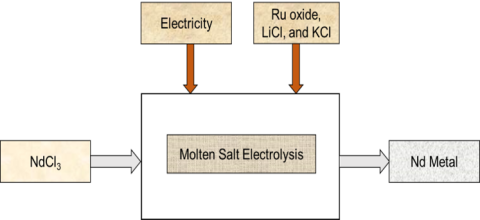
Techno-economic analysis and life cycle assessment of Nd metal reduction using dimensionally stable anode (DSA) based molten salt electrolysis (MSE) versus conventional fluoride-based MSE.
Achievement
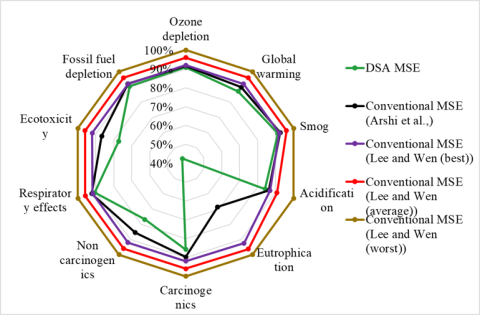
- For 1kg of Nd metal produced, global warming potential (GWP) estimated at 136 kg CO2 eq for DSA-based MSE vs 141-156 kg CO2 eq for conventional MSE (Fig. 2).
- Reusing Ru oxide coating by 1000 hrs is desirable maximum time.
- Break-even cost for DSA-based MSE estimated $21-$27 per kg of Nd metal, excluding input Nd oxide cost.
Significance and Impact
Technology enables continuous production of Nd metal, while consuming 34% less specific energy in electrolytic cell and eliminating direct emissions of CO2 and perfluorocarbons compared with conventional MSE.
Hub Target Addressed
Supporting environmentally sustainable critical material processing.