CMI researchers at Ames National Laboratory conducted the activity for highlight
Innovation
Direct conversion of neodymium oxide into high-purity Nd2Fe14B powders with low oxygen content, by calciothermic reduction-diffusion process (Ca-RD).
Achievement
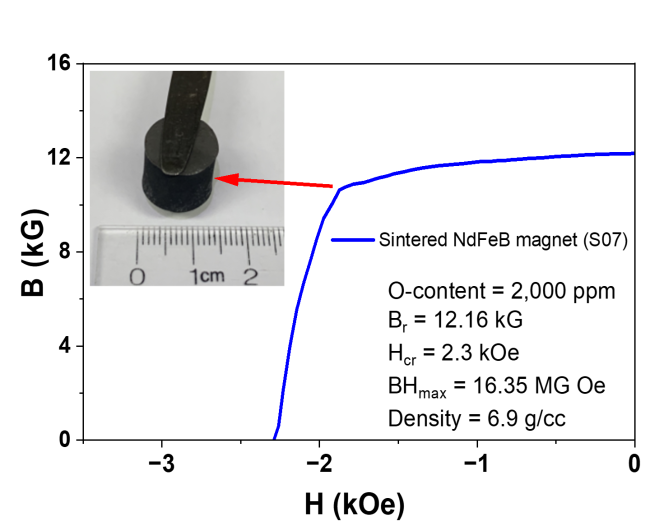
By reducing oxidation via larger Fe particles and modified washing, we produced NdFeB powders suitable for sintering. The sintered magnet directly produced from this material has an energy product of 16 MGOe with Br = 12 kG and density 6.9 g/cc (see figure).
Significance and Impact
One-step calciothermic procedure circumvents the neodymium metallization process through direct production of Nd2Fe14B permanent magnets from Nd2O3 and Fe, paving a way for domestic permanent magnet production. Our innovation brings us one step closer to producing industry standard NdFeB powders by direct metallization.
Hub Target Addressed
Energy efficient rare earth metals production.