CMI researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Idaho National Laboratory and Pennsylvania State University worked on the research that led to this highlight and was published in Inorganic Chemistry in July 20, 2020
Achievements
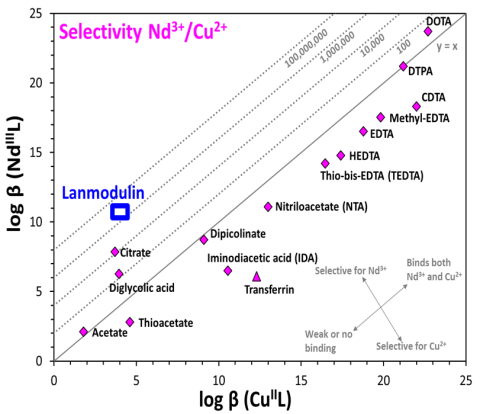
Demonstrated the utility of Lanmodulin (LanM), a natural protein from a Methylotrophic bacterium, for REE recovery from electronic waste.
Significance and impact
Use of LanM offers a new and more sustainable avenue for REE recovery. The newly discovered LanM displays high REE binding affinity and extreme REE selectivity even at low pH (down to ~3), overcoming a major limitation for protein application in metal extraction.
Details and next steps
Demonstration of a one-step, all aqueous process for selective REE recovery through ligand immobilization and column purification.
