CMI researchers at Idaho National Laboratory conducted the research for this highlight
Achievement
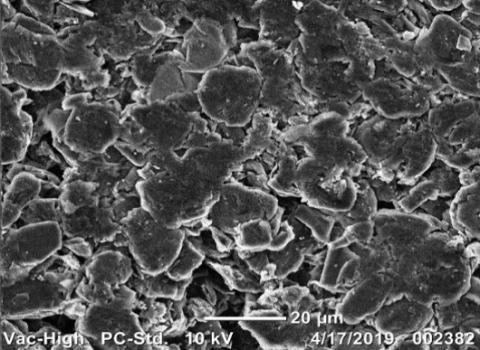
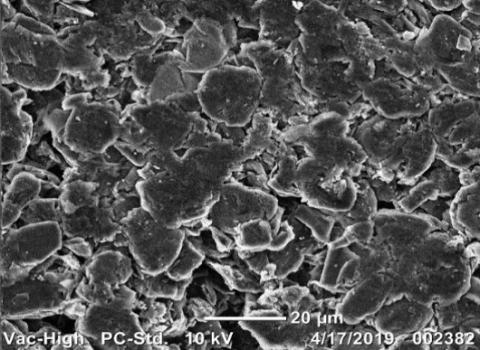
Graphite recovered after electrochemical leaching (E-Leach) shows comparable capacity and cyclability with commercial graphite. Results after the recovered graphite was sintered at 600 °C to remove amorphous carbon and other organic material.
Significance and impact
- Graphite recovered as by-product of E-Leach has the potential to be re-used as battery anode
- Graphite as by-product of the co-recovery of Co, Mn, Li, and Ni can generate an additional revenue stream for the comprehensive recycling flowsheet
Details
- Flake structure (B) of the recycled graphite may be a feature of the source of recycled batteries and better performance may be achieved after surface treatment
- Analysis of a battery cell, completely made of recycled material is proposed for Q16