Scientific Achievement
- Discovery of a new catalytic route to convert various polyethylene grades directly to alkylaromatic liquids
- The simple, scalable, robust, one-pot process requires no solvent or exogeneous H2 and operates at moderate temperature (< 300 °C)
Significance and Impact
- environmental benefits in low-carbon route to aromatic chemicals and energy-dense liquid fuels
- economic value in use of a high volume commodity plastic as a feedstock
- plastic waste reuse decreases environmental inputs
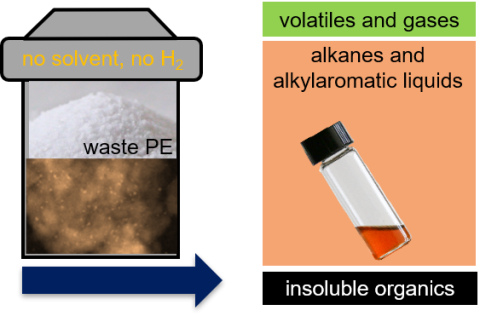
Research Details
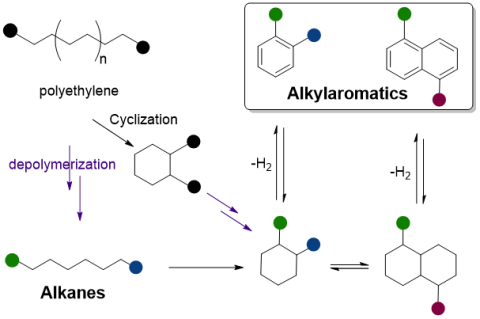
- tandem reactions precisely couple endothermic aromatization with exothermic C-C bond hydrogenolysis
- the molecular weight distribution narrows during depolymerization as liquid dialkylaromatics form
This research was a collaboration between UC Santa Barbara, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign,and Cornell University. Supported by award DE-AC-02-07CH11358 Catalysis for Polymer Upcycling (subcontract from Ames Laboratory).
Zhang, Zeng, Yappert, Sun, Lee, Lapointe, Peters, Abu-Omar, Scott, Science, 2020, 370, 447-441. DOI: 10.1126/science.abc5441
Zhang, Zeng, Abu-Omar, Scott, US Patent Application 63/052,277 (filed 7/15/2020).
