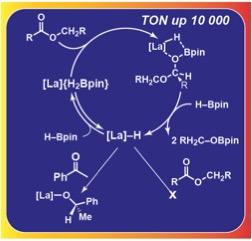
The high catalytic reactivity of homoleptic tris(alkyl) lanthanum La{C(SiHMe2 )3 }3 is highlighted by C-O bond cleavage in the hydroboration of esters and epoxides at room temperature. The catalytic hydroboration tolerates functionality typically susceptible to insertion, reduction, or cleavage reactions. Turnover numbers (TON) up to 10 000 are observed for aliphatic esters. Lanthanum hydrides, generated by reactions with pinacolborane, are competent for reduction of ketones but are inert toward esters. Instead, catalytic reduction of esters requires activation of the lanthanum hydride by pinacolborane.
Patnaik, S.; Sadow, A. D., Interconverting Lanthanum Hydride and Borohydride Catalysts for C=O Reduction and C−O Bond Cleavage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2505-2509.
