 A team of scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Ames National Laboratory and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory has provided new data and analysis on infinite-layer nickelates. This material is a recently discovered class of unconventional superconductors. The results provide new insights into how these superconductors work and how they differ from other superconductors.
A team of scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Ames National Laboratory and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory has provided new data and analysis on infinite-layer nickelates. This material is a recently discovered class of unconventional superconductors. The results provide new insights into how these superconductors work and how they differ from other superconductors.
Superconductivity is when a material conducts electricity without energy loss below a critical temperature. Superconductors are used in technology such as MRI machines and quantum computers.
There are two types of superconductors, conventional and unconventional. The main difference between the two types is the critical temperature. Conventional superconductors usually work at ultra-low temperatures. Many unconventional superconductors work at higher (though still very low) temperatures. Researchers seek higher temperatures to open up new uses for superconductors, but also to reveal the mechanisms that give rise to these unconventional behaviors.
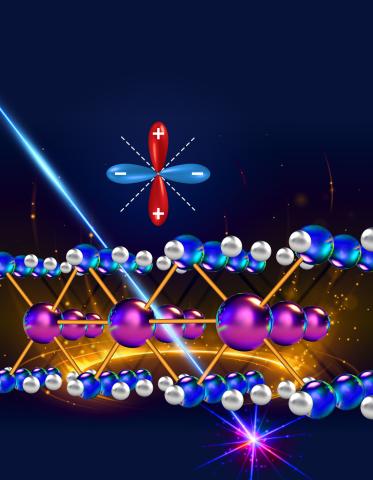
According to Jigang Wang, a scientist at Ames Lab, superconductors are also different at the electronic level. When a superconductor reaches its critical temperature, electron pairs called Cooper pairs are formed. These Cooper pairs create a superconducting gap. This gap is the minimum energy needed to get electrons moving individually. In conventional superconductors, the gap is the same size in all directions (for example, in s-wave superconductivity). However, in unconventional superconductors, the gap size may be different depending on the direction electrons are flowing (for example, in d-wave superconductivity).
“One of the most recent and potentially groundbreaking unconventional superconductors are infinite-layer nickelates,” said Bing Cheng, a postdoctoral researcher in Wang’s Lab. This material was originally discovered by Harold Hwang at SLAC, also part of the research team.
Infinite-layer nickelates are extremely thin and complex, existing as films on other materials. These properties make it difficult to use the conventional tools for investigating the fundamental properties of these superconductors. To address this challenge, Wang’s team at Ames Lab used their expertise in terahertz-wave spectroscopy to examine the nickelates. With these tools, they measured the gap sizes and discovered fast superconducting fluctuations when the material is near or above its critical temperature.
Their results confirmed the material has a d-wave superconductivity, which is similar to some unconventional superconductors identified by Zhi-Xun Shen, a member of the team from Stanford University. Shen has dedicated more than three decades to unraveling the secrets of d-wave superconductivity.
According to Wang, understanding the nature of unconventional superconductivity is still one of the biggest challenges in condensed matter and materials physics today. “There are still debates on what glues the electrons in Cooper pairs,” he said. However, understanding these nickelates could offer a solution to this long-standing puzzle.
This research is further discussed in “Evidence for d-wave superconductivity of infinite-layer nickelates from low-energy electrodynamics,” written by Bing Cheng, Di Cheng, Kyuho Lee, Liang Luo, Zhuoyu Chen, Yonghun Lee, Bai Yang Wang, Martin Mootz, Ilias E. Perakis, Zhi-Xun Shen, Harold Y. Hwang, and Jigang Wang, and published in Nature Materials.
This work was supported by the DOE Office of Science (Office of Basic Energy Sciences).
Ames National Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science National Laboratory operated by Iowa State University. Ames Laboratory creates innovative materials, technologies, and energy solutions. We use our expertise, unique capabilities, and interdisciplinary collaborations to solve global problems.
Ames Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit https://energy.gov/science.
