Scientific Achievement:
Combination of ligand design and solid-state (SS) NMR establishes highly reactive, uniform surface dialkyl lanthanide species. Reactions with pinacolborane give catalytically active species for C–O bond cleavage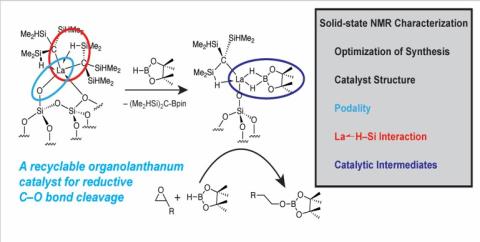 by hydroboration, identified by 11B, 13C and 29Si SS NMR.
by hydroboration, identified by 11B, 13C and 29Si SS NMR.
Significance and Impact:
A new class of highly active and recyclable catalysts leverage lanthanide oxophilicity and robust silica-lanthanide bonding to enable facile C–O bond cleavage reactions in transformations of oxygenated organic species for applications in hydroboration of epoxides.
Research Details:
Wang, Z.; Patnaik, S.; Eedugurala, N.; Manzano, J. S.; Slowing, I. I.; Kobayashi, T.; Sadow, A. D.; Pruski, M., Silica-Supported Organolanthanum Catalysts for C–O Bond Cleavage in Epoxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2935-2947. doi:10.1021/jacs.9b11606
