Pressure dependence of magnetic fluctuations in the spin triplet superconductor candidate UTe2 was investigated by nuclear magnetic resonance technique.
Scientific Achievement:
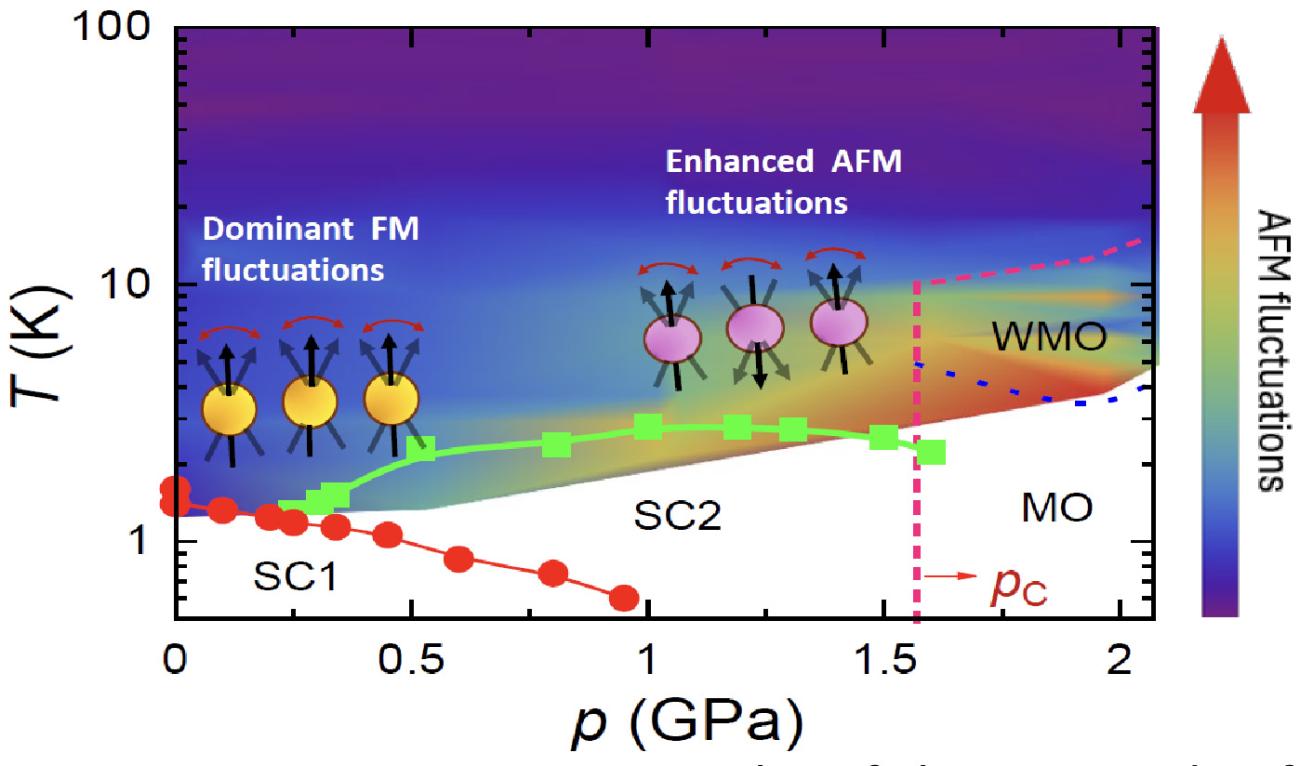
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements on the spin triplet superconductor candidate UTe2 revealed the coexistence of antiferromagnetic (AFM) and ferromagnetic (FM) fluctuations, where the AFM fluctuations are enhanced with increasing pressure.
Significance and Impact:
This is the first microscopic experimental evidence characterizing the evolution of magnetic fluctuations under pressure in UTe2. This provides important insights into the mechanism of superconductivity (SC) in multi-SC phases.
Research Details:
- 125Te nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of UTe2 under various pressures ranging from 0 to 2.05 GPa in a wide temperature range of T = 1.5 – 300 Kelvin.
- UTe2 is the recently discovered spin-triplet superconductor and shows multiple superconducting phases (SC1 and SC2 shown in the figure).
Devi Vijayan Ambika, Qing-Ping Ding, Corey E. Frank, Sheng Ran, Nicholas P. Butch, and Yuji Furukawa, Physical Review B, 113, 014510 (2026). Editors’ suggestion. https://doi.org/10.1103/4gcm-mbl7
