Scientific Achievement
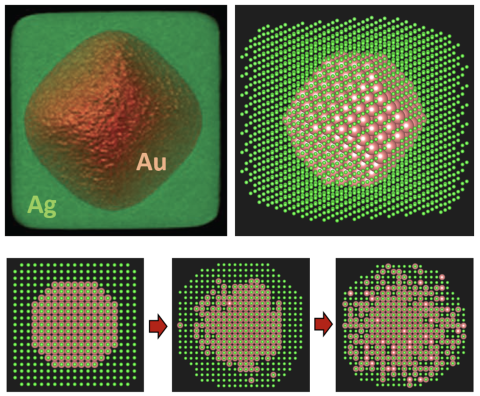
Our theoretical formulation for vacancy-mediated intermixing in bimetallic core-shell nanocrystals incorporates for the first time realistic kinetics (and thermodynamics). It allows prediction of the effective activation barrier and the time scale for intermixing.
Significance and Impact
Core-shell vs monometallic NCs allow finer tuning of properties, e.g., for catalysis. Our formulation allows reliable assessment of their stability against intermixing (a process which would degrade their properties).
Research Details
- Our stochastic model utilizes two classes of interactions to reliably determine activation barriers for atoms hopping between crystalline sites for any local environment.
- KMC simulation precisely determines model behavior
- Validation: We recover time-scales observed in experiment for intermixing in Au octahedral core – Ag cubic shell NCs.
Reference: Y. Han and J.W. Evans, ACS Nano 2024, 18, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.4c06435 + Suppl. Cover
USDOE NERSC resources were used for some computations
