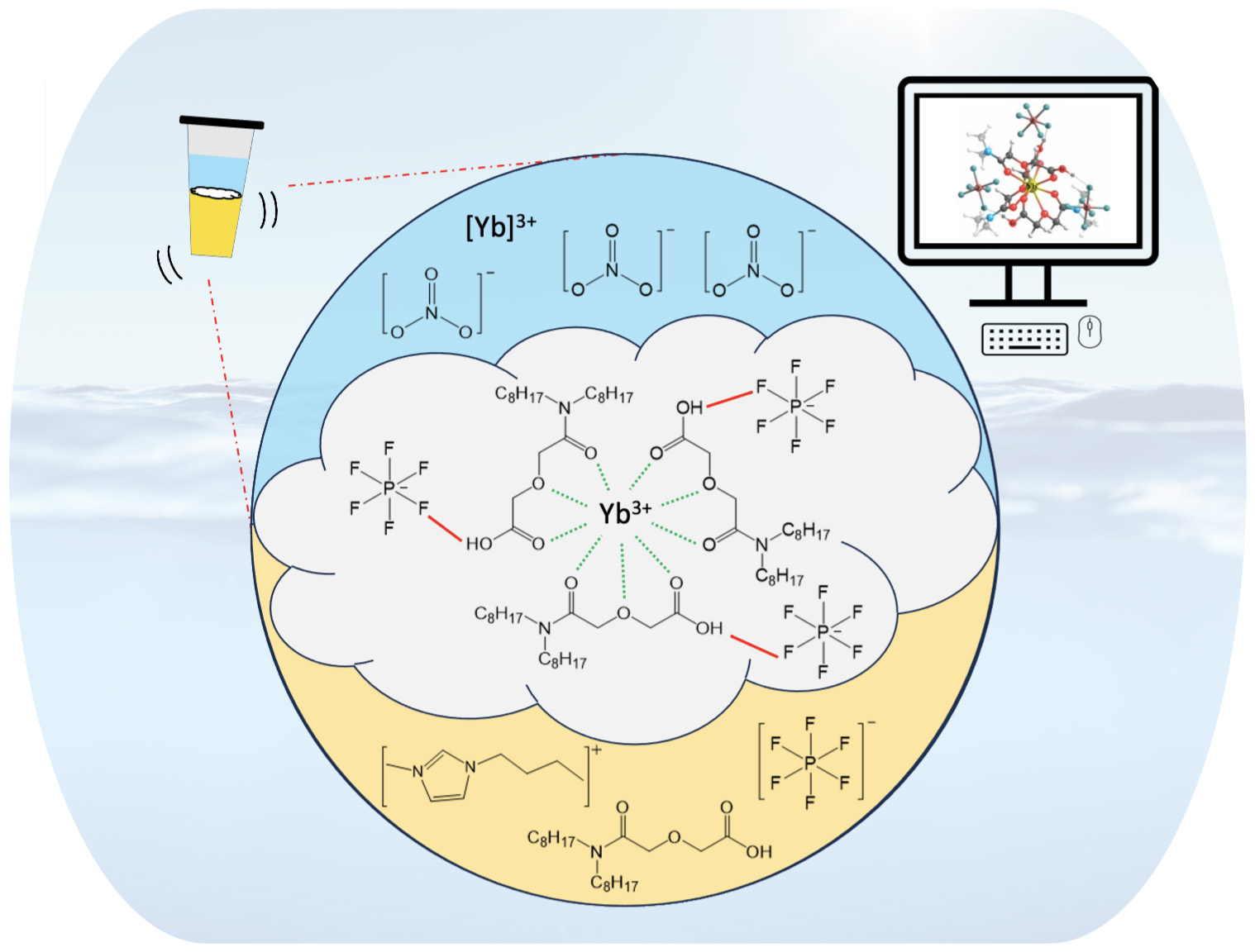
A fundamental study into the molecular interactions between the REE ([Yb3+]), extractant (DODGAA), and the ionic liquid [BMIM+][PF6-] offers insight into the ensuing extraction mechanism that leads to precipitate formation.
Precipitation offers a highly efficient approach for REE recovery, allowing for single-step solid-liquid separation and boosting recovery efficiency and sustainability. This study advances the understanding of REE extraction mechanisms using ionic liquids and provides strategies to optimize experimental conditions and assess scalability for industrial-scale applications.
- The Yb-DODGAA complex is confirmed via ATR-FTIR, SEM-EDS, and DSC-TGA techniques, and involves the [PF6-] anion as the counter anion.
- Hydrogen bonding between the fluorine atom of [PF6-] and the -OH moiety of DODGAA is critical for precipitate formation.
- Computational studies were also conducted to examine the coordination environment of metal-extractant complexes by analyzing the binding affinity.
Shu-An Hsieh, Tamalika Ash, Theresa L. Windus, Dapeng Jing, Tanya Prozorov, and Jared L. Anderson. "Using Diglycolamide Extractants in an Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid for Rare Earth Element Extraction and Recovery." ACS Omega (2024) 9, 40134−40144. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.4c06091
Work was performed at Ames National Laboratory. The computational calculations were performed with a grant of computer time at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Centre (NERSC).
