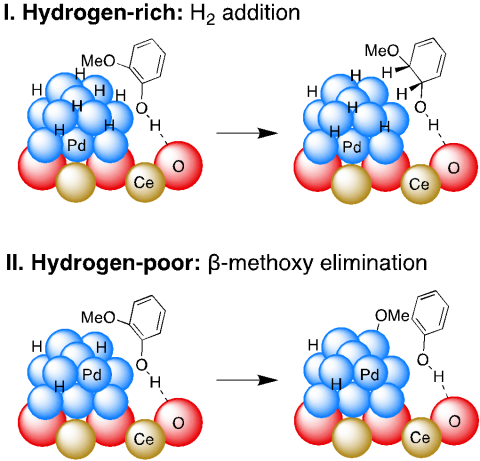
The conversion of guaiacol into the nylon precursors, cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone, is catalyzed by palladium supported on high surface area ceria (Pd/HS CeO2) under mild conditions (100 °C, ≤1 bar H2) via sequential hydrodemethoxylation and hydrogenation.
In contrast, the 2-methoxycyclohexanol side product is generated by direct guaiacol hydrogenation.
Reaction selectivity is determined by competing C-O bond hydrogenolysis versus arene hydrogenation.
Hydrogenolysis selectivity increases as H2 pressure decreases, and over 80 % H2 is incorporated into the products at 1 bar H2.
Higher reactivity of guaiacol than anisole implies that the hydroxyl group is essential in Pd/HS CeO2 catalysis.
The combination of near quantitative mass balance of H2, high recyclability, and use of water as a solvent offers a simple, green and efficient conversion of lignin-derived aromatics into commercial products.
Zhou, H., Wang, H., Sadow, A.D., Slowing, I.I. “Toward hydrogen economy: Selective guaiacol hydrogenolysis under ambient hydrogen pressure.” Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2020, 270, 118890.
