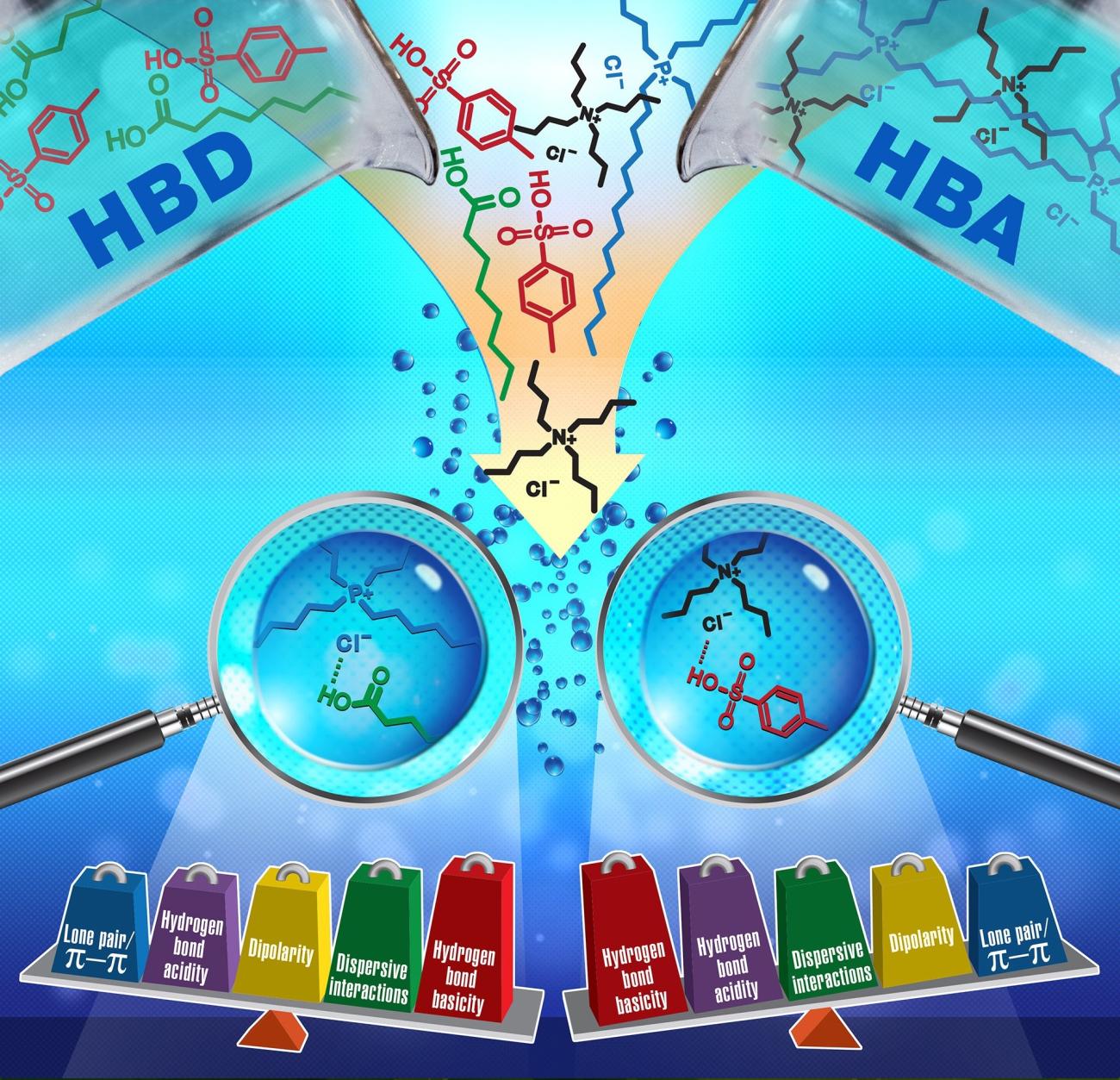
Deep eutectic solvents comprised of ammonium/phosphonium salts and carboxylic acids have been characterized by inverse gas chromatography to understand their solvation interactions. Solute-solvent interactions are beneficial in understanding the performance of DESs in various chemical separations and catalysis.
First study to chromatographically measure the solute-solvent interactions of deep eutectic solvents. This approach overcomes the limitations of solvatochromic probes such as reaction of acidic hydrogen bond donors with betaine dye 30.1.
- Solvation properties of 20 DESs have been characterized.
- Effect of structural composition including molar ratio of HBA/HBD, length of HBA and HBD alkyl chain substituent, structure and combination of HBA cation and anion, and pKa of HBD on the solvation properties have been studied.
- Solvation interactions have been used to interpret the performances of DESs in extraction of natural products and desulfurization of fuels.
Farooq, M. Q.; Odugbesi, G. A.; Abbasi, N. M.; Anderson, J. L. “Elucidating the Role of Hydrogen Bond Donor and Acceptor on Solvation in Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Ammonium/Phosphonium Salts and Carboxylic Acids.” ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 18286–18296