Solvation properties of active pharmaceutical ingredient-based deep eutectic solvents (API-DESs) were systematically studied. API-DESs were classified into different groups using their individual solvation interactions. Grouping of API-DESs can be used to interpret and explain their behavior in various chemical separations and material science.
The solute-solvent interactions of API-DESs were chromatographically evaluated for the first time. Fundamental insights towards the solvation behavior of API-DESs can help in their rational design for energy intensive separation processes.
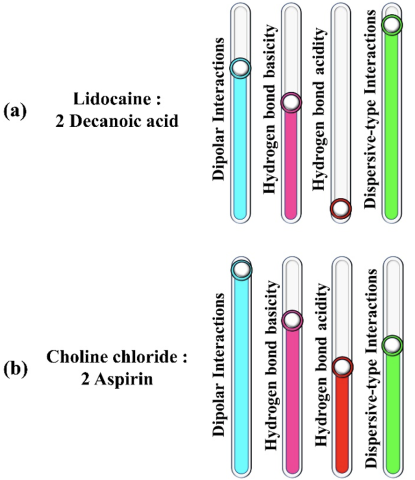
- DESs comprised of ionic hydrogen bond acceptors (HBAs) and API hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) offered higher dipolar interactions, hydrogen bond basicity, and acidity compared to DESs containing API-HBAs and non-ionic HBDs.
- Individual solvation interactions of DESs with probe molecules resulted in a change in analyte elution order and their separation selectivity.
- API-DESs can be classified into four clusters based on their dipolarity/polarizability and hydrogen bond basicity.
Farooq, M.Q.; Abbasi, N.M.; Smith, E.A.; Petrich, J.W.; Anderson, J.L. “Characterizing the Solvation Characteristics of Deep Eutectic Solvents Composed of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients as a Hydrogen Bond Donor and/or Acceptor” ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 3066–3078
