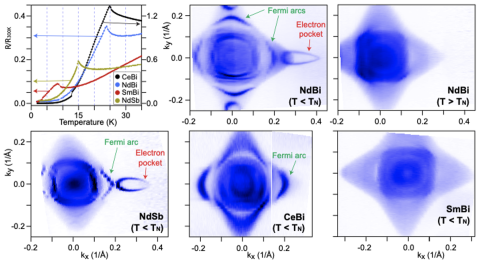
ARPES measurements show that the RBi and RSb family of materials host magnetic Fermi arcs and the energy of the band splitting scales with the magnetic moments of the rare-earths.
Significance and Impact
This experimentally accessible family of compounds with novel magnetic surface states suggests that other antiferromagnets may exhibit similar spin textured Fermi arcs and magnetic splitting that are deemed important for development of future spintronic devices.
Research Details
- Single crystals were studied using transport, magnetization and ARPES.
- These states split into hole- and electron-like bands that form Fermi arcs with opposing spin textures.
Yevhen Kushnirenko, Benjamin Schrunk, Brinda Kuthanazhi, Lin-Lin Wang, Junyeong Ahn, Evan O'Leary, Andrew Eaton, S. L. Bud'ko, Robert-Jan Slager, P. C. Canfield, and Adam Kaminski, Phys. Rev. B (Editor’s Suggestion): 106, 115112 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.106.115112
